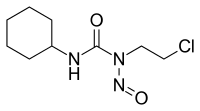
Lomustine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | CeeNU, Gleostine, CCNU, others |
| Other names | 1-(2-chloroethyl)-3-cyclohexyl-1-nitrosourea |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Alkylating agent[1] |
| Main uses | Brain tumors, melanoma, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL)[1][2] |
| Side effects | Pulmonary fibrosis, low platelets, low white blood cells, low red blood cells, nausea, kidney problems, liver problems[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth (capsules) |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682207 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | ~100% |
| Protein binding | 50% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Metabolites | Monoxydroxylated metabolites, trans-4-hydroxy-CCNU, cis-4-hydroxy-CCNU[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 16–48 hours (metabolites) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H16ClN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 233.70 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 90 °C (194 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Lomustine sold under the brand name CeeNU, is a medication used to treat brain tumors, melanoma, and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).[1][2] In HL it is used when other treatments have not worked.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include pulmonary fibrosis, low platelets, low white blood cells, low red blood cells, nausea, kidney problems, and liver problems.[1] Other side effects may include hair loss, confusion, vision loss, and mouth inflammation.[2] It should not be used in pregnancy or breastfeeding.[2] It is an alkylating nitrosourea compound.[1]
Lomustine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1976.[1] It is available as a generic medication.[2] In the United States it costs about 1,050 USD per 100 mg pill as of 2021.[4] This amount in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about £50.[2]
Medical uses
Dosage
By itself it is used at a dose of around 120 to 130 mg/m2 every 6 to 8 weeks.[2]
Mechanism of action
It is closely related to semustine and is in the same family as streptozotocin. It is a highly lipid-soluble drug,[5] thus it crosses the blood-brain barrier. Lomustine has a long time to nadir (the time when white blood cells reach their lowest number). It is a monofunctional alkylating agent, alkylates both DNA and RNA, has the ability to cross-link DNA.[6] As with other nitrosoureas, it may also inhibit several key enzymatic processes by carbamoylation of amino acids in proteins.[7] Lomustine is cell-cycle nonspecific.
Society and culture
Price
In the U.S., the patent for lomustine has expired, but only one company manufactures it. In 2013, Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. sold its CeeNU brand of lomustine to CordenPharma, a subsidiary of International Chemical Investors S.E., which markets it as Gleostine through NextSource Biotechnology. In 2013, BMS charged $50 a capsule. In 2018, NextSource charged $768 a capsule. Some doctors said the price increase made it unaffordable, and one doctor called it "price gouging."[8][9][10]
Other animals
It has also been used in veterinary practice as a treatment for mast cell tumors in dogs.[11]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Lomustine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 17 August 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 941. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ Lee FY, Workman P, Roberts JT, Bleehen NM (1985). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of oral CCNU (lomustine)". Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology. 14 (2): 125–31. doi:10.1007/bf00434350. PMID 3971475. S2CID 29619378.
- ↑ "Gleostine Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- ↑ "BC Cancer Agency Cancer Drug Manual. Lomustine (CCNU; CeeNU)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 August 2019. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ↑ Pizzo PA, Poplack DG, eds. (2006). Principles and Practice of Pediatric Oncology (5th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 300. ISBN 9780781754927.
- ↑ "Gleostine (lomustine) Capsules, for Oral Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). NextSource Biotechnology, LLC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ↑ Cancer Drug Price Rises 1400% With No Generic to Challenge It Archived 2018-07-31 at the Wayback Machine, Peter Loftus, The Wall Street Journal, 12/26/2017 [FREE]
- ↑ "NextSource Biotechnology Gains FDA Approval for Use of Tradename Gleostine (lomustine), an Anti-Cancer Chemotherapy Agent". www.prnewswire.com. NextSource Biotechnology. Archived from the original on 19 August 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ↑ "Gleostine (lomustine) Capsules — Healthcare Providers". NextSource Biotechnology. Archived from the original on 23 June 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ↑ Weiss DJ, Wardrop KJ, Weiss D (2010). Schalm's Veterinary Hematology (6 ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Incorporate d. p. 487. ISBN 978-0-8138-0896-3.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- CeeNu (lomustine) Capsules Archived 2016-10-23 at the Wayback Machine data sheet published by the FDA
- Lomustine at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Diseases Database (DDB): 29525