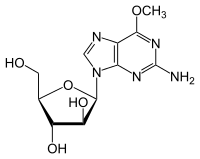
Nelarabine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Arranon, Atriance |
| Other names | 506U78 |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Antimetabolite[1] |
| Main uses | Acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoma[2] |
| Side effects | Bone marrow suppression, sleepiness, headache, numbness, fever, swelling, vomiting[2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Intravenous |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607077 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | <25% |
| Metabolism | By adenosine deaminase, to 9-β-D-arabinofuranosylguanine |
| Elimination half-life | 30 minutes (nelarabine) 3 hours (ara-G) |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 297.271 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Nelarabine, sold under the brand names Arranon and Atriance , is a medication used to treat T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL).[2] It is used when other treatments are not effective.[2] It is given by gradual injection into a vein.[2]
Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, sleepiness, headache, numbness, fever, swelling, and vomiting.[2] Other side effects may include confusion, seizures, tumor lysis syndrome, and peripheral neuropathy.[2] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[2] It is an antimetabolite which replaces guanine and interferes with the making of new DNA.[1]
Nelarabine was approved for medical use in the United States and Europe in 2005.[5][1] In the United Kingdom six vials of 250 mg cost the NHS about £1,300 as of 2021.[6] In the United States this amount costs about 4,600 USD.[7] A generic version was approved in 2021 in the USA.[8]
Medical uses
Dosage
In adults it is used at a dose of 1500 mg/m2 on day 1, 3, and 5 out of 21 days.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 "Atriance". Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Nelarabine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ "Arranon- nelarabine injection". DailyMed. 11 June 2020. Archived from the original on 17 October 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- ↑ "Atriance EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- 1 2 "DailyMed - ARRANON- nelarabine injection". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 17 October 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 960. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Arranon Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ Research, Center for Drug Evaluation and (10 February 2022). "2021 First Generic Drug Approvals". FDA. Archived from the original on 21 June 2022. Retrieved 22 October 2022.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
- "Nelarabine". NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. National Cancer Institute. Archived from the original on 2020-04-12. Retrieved 2021-03-03.
- "Nelarabine". National Cancer Institute.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)