Pentostatin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nipent |
| Other names | 2'-deoxycoformycin (DCF) |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Purine antagonist[1] |
| Main uses | Hairy cell leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), cutaneous T-cell lymphoma[1] |
| Side effects | Nausea, fever, rash, cough, shortness of breath, itchiness, headache, low blood cells[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Intravenous |
| Typical dose | 4 mg/m2[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a692004 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | 4% |
| Metabolism | Liver, minor |
| Elimination half-life | 2.6 to 16 hours, mean 5.7 hours |
| Chemical and physical data | |
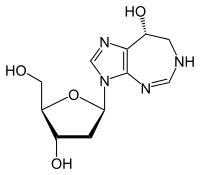
| Formula | C11H16N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 268.273 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Pentostatin, sold under the brand name Nipent, is a medication used to treat hairy cell leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.[1][2] It is given by injection into a vein.[1]
Common side effects include nausea, fever, rash, cough, shortness of breath, itchiness, headache, and low blood cells.[1] Other side effects may include seizures, coma, kidney problems, lung toxicity, and infection.[1] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[1] It is a purine antagonist.[1]
Pentostatin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1991.[1] In the United Kingdom 10 mg of medication costs the NHS about £730 as of 2021.[3] This amount in the United States is about 2,300 USD.[4]
Medical uses
Pentostatin is used to treat hairy cell leukemia.[5] It is given by intravenous infusion once every two weeks for three to six months.
Additionally, pentostatin has been used to treat steroid-refractory acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease.[6]
Pentostatin is also used in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients who have relapsed.
Dosage
It may be used at a dose of 4 mg/m2 every two weeks.[1]
Mechanism
It is classified as a purine analog, which is a type of antimetabolite.
It mimics the nucleoside adenosine and thus inhibits the enzyme adenosine deaminase, interfering with the cell's ability to process DNA.[7]
Cancer cells generally divide more often than healthy cells; DNA is highly involved in cell division (mitosis) and drugs which target DNA-related processes are therefore more toxic to cancer cells than healthy cells.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Pentostatin Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 16 August 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2021.
- ↑ "DailyMed - NIPENT- pentostatin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2021.
- ↑ BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 964. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Nipent Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 24 January 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2021.
- ↑ Cannon T, Mobarek D, Wegge J, Tabbara IA (October 2008). "Hairy cell leukemia: current concepts". Cancer Invest. 26 (8): 860–5. doi:10.1080/07357900801965034. PMID 18798068.
- ↑ Bolaños-Meade J, Jacobsohn DA, Margolis J, Ogden A, Wientjes MG, Byrd JC, Lucas DM, Anders V, Phelps M, Grever MR, Vogelsang GB (April 2005). "Pentostatin in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease". J Clin Oncol. 23 (12): 2661–8. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.06.130. PMID 15837980.
- ↑ Sauter C, Lamanna N, Weiss MA (September 2008). "Pentostatin in chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 4 (9): 1217–22. doi:10.1517/17425255.4.9.1217. PMID 18721115.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|