2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitroamphetamine
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitroamphetamine (DON) is a psychedelic drug and amphetamine. It is an analog of DOM and DOB. It is also closely related to 2C-N.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
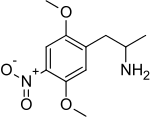
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)propan-2-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H16N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 240.259 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 206 to 207 °C (403 to 405 °F; 479 to 480 K) (hydrochloride) 231-232 °C ((R)-isomer)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Chemistry
DON is in a class of compounds commonly known as alpha-methyl phenethylamines, or amphetamines and the full chemical name is 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)propan-2-amine. It has a stereocenter.
Effects
In his book PiHKAL, Alexander Shulgin lists a dosage of DON as being 3-4.5 mg orally with amphetamine-like stimulation lasting 8–15 hours.[1]
Dangers
The toxicity of DON is not known.
Legality
DON is unscheduled in the United States, but because of its close similarity in structure and effects to DOM and DOB, possession and sale of DON may be subject to prosecution under the Federal Analog Act. DON is listed as a Class A drug in the Drugs controlled by the UK Misuse of Drugs Act after the table of contents of PiHKAL and TiHKAL were added to the schedules.
See also
References
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||