Belzutifan
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | bell-ZOO-ti-fan |
| Trade names | Welireg |
| Other names | MK-6482, PT2977 |
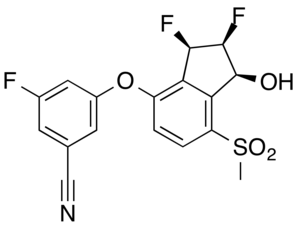
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Antineoplastic |
| Main uses | von Hippel–Lindau disease associated cancer[1] |
| Side effects | Low hemoglobin, tiredness, kidney problems, headache, dizziness, increased blood sugar, nausea[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Typical dose | 120 mg OD[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H12F3NO4S |
| Molar mass | 383.34 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Belzutifan, sold under the brand name Welireg, is a medication used to treat von Hippel–Lindau disease-associated renal cell carcinoma, central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastoma, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (pNET).[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include low hemoglobin, tiredness, kidney problems, headache, dizziness, increased blood sugar, and nausea.[1] Other side effects may include low oxygen.[1] Use during pregnancy may harm the baby.[1] It is an hypoxia-inducible factor 2α inhibitor.[1][4]
Belzutifan was approved for medical use in the United States in 2021.[1] In the United Kingdom a month of treatment costs the NHS about £12,000 as of 2022.[4] This amount in the United States costs about 28,000 USD.[5] It is not yet available in Europe.[4]
Medical uses
Belzutifan is indicated for treatment of adults with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease who require therapy for associated renal cell carcinoma (RCC), central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastomas, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET), not requiring immediate surgery.[3] Belzutifan was also found to be efficacious in an adolescent who had Pacak–Zhuang syndrome with polycythemia and paragangliomas.[6]
Dosage
It is generally taken at a dose of 120 mg once per day.[1]
History
Belzutifan is the first drug to be awarded an "innovation passport" from the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).[7][8] Belzutifan is the first hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha inhibitor therapy approved in the U.S.[9]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Welireg- belzutifan tablet, film coated". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 28 October 2022. Retrieved 12 September 2021.
- ↑ "WELIREG" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 October 2022. Retrieved 28 October 2022.
- 1 2 "FDA approves belzutifan for cancers associated with von Hippel-Lindau". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 13 August 2021. Archived from the original on 13 August 2021. Retrieved 13 August 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 3 "Belzutifan". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 18 March 2021. Archived from the original on 26 April 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ↑ "Welireg Prices, Coupons, Copay & Patient Assistance". Drugs.com. Retrieved 28 October 2022.
- ↑ Kamihara, Junne; Hamilton, Kayla V.; Pollard, Jessica A.; Clinton, Catherine M.; Madden, Jill A.; Lin, Jasmine; Imamovic, Alma; Wall, Catherine B.; Wassner, Ari J.; Weil, Brent R.; Heeney, Matthew M. (25 November 2021). "Belzutifan, a Potent HIF2α Inhibitor, in the Pacak–Zhuang Syndrome". New England Journal of Medicine. 385 (22): 2059–2065. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110051. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 34818480. S2CID 244651726. Archived from the original on 28 October 2022. Retrieved 2 October 2022.
- ↑ "First Innovation Passport awarded to help support development and access to cutting-edge medicines". Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) (Press release). 26 February 2021. Archived from the original on 14 August 2021. Retrieved 14 August 2021.
- ↑ "MHRA awards first 'innovation passport' under new pathway". RAPS (Press release). Archived from the original on 26 April 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Merck's Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2 Alpha (HIF-2α) Inhibitor Welireg (belzutifan) for the Treatment of Patients With Certain Types of Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) Disease-Associated Tumors" (Press release). Merck. 13 August 2021. Archived from the original on 13 August 2021. Retrieved 13 August 2021 – via Business Wire.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
- Clinical trial number NCT04195750 for "A Study of Belzutifan (MK-6482) Versus Everolimus in Participants With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (MK-6482-005)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03401788 for "A Phase 2 Study of Belzutifan (PT2977, MK-6482) for the Treatment of Von Hippel Lindau (VHL) Disease-Associated Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) (MK-6482-004)" at ClinicalTrials.gov