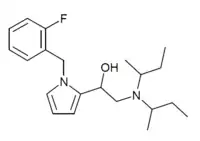
2F-Viminol
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H31FN2O |
| Molar mass | 346.490 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
2F-Viminol is a pyrrole derived opioid analgesic drug, which was originally developed by a team at the drug company Zambon in the 1960s. It is around twice as potent as the parent compound viminol, though unlike viminol, 2F-viminol has never passed clinical trials or been approved for medical use. 2F-Viminol has been sold as a designer drug, first being identified in Sweden in 2019.[1] It is one of a number of structurally atypical opioid agonists to have appeared on the designer drug grey-market since broad controls over fentanyl analogues were introduced in China in 2015.[2] It was made illegal in Sweden in August 2019 and in Latvia in November 2019.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Ordinance banning certain products that are harmful to health". Swedish Code of Statutes. 4 July 2019.
This Ordinance enters into force on 6 August 2019
- ↑ Bao Y, Meng S, Shi J, Lu L (July 2019). "Control of fentanyl-related substances in China". The Lancet. Psychiatry. 6 (7): e15. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30218-4. PMID 31230685.
- ↑ "SPKC nosaka aizliegumu vielām 2F-viminol, furanyl UF – 17 un to saturošiem izstrādājumiem" [SPKC bans 2F-viminol, furanyl UF-17 and products containing them]. Slimību profilakses un kontroles centrs (Center for Disease Prevention and Control) (in Latvian). 6 November 2019.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.