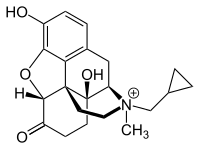
Methylnaltrexone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Relistor |
| Other names | Naltrexone-methyl-bromide, methylnaltrexone bromide |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Peripherally acting μ-opioid receptor antagonist[1] |
| Main uses | Constipation due to opioids[2] |
| Side effects | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, dizziness, nausea, opioid withdrawal[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of use | By mouth, intravenous, subcutaneous |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608052 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | 11–15.3% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 8 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (50%), faeces (50%) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26NO4 |
| Molar mass | 356.442 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Methylnaltrexone (MNTX), sold under the brand name Relistor, is a medication used to treat constipation due to opioids.[2] It may be used when other laxatives are not effective.[1] It is taken by mouth or by injection under the skin.[2]
Common side effects include abdominal pain, diarrhea, dizziness, nausea, and opioid withdrawal.[1] Other side effects may include gastrointestinal perforation.[2] It a peripherally acting μ-opioid receptor antagonist, which means it does not generally affect the central pain reducing effects of other opioids.[1]
Methylnaltrexone was approved for medical use in the United States in 2008.[2] In the United Kingdom the injectable formulation costs the NHS about £21 per dose as of 2021.[1] In the United States this amount costs about 150 USD.[4]
Medical uses
Methylnaltrexone is approved for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation (OIC). It is generally only to be used when ordinary laxatives have failed.
Dosage
It is given at a dose of 450 mg by mouth per day or 12 mg injected under the skin per day.[2]
Mechanism of action
Methylnaltrexone binds to the same receptors as opioid analgesics such as morphine and oxycodone, but it acts as an antagonist, blocking the effects of those analgesics mainly on the peripheral opioid receptors, specifically the constipating effects on the gastrointestinal tract. Furthermore, as methylnaltrexone cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, it does not reverse the pain-killing properties of opioid agonists or cause withdrawal symptoms, but since a small portion of analgesia comes from the peripheral opioid receptors, it can increase pain from inflammatory conditions such as arthritis. Methylnaltrexone is unable to enter the brain primarily because it carries a positive charge on its nitrogen atom. This is the primary characteristic that makes methylnaltrexone behave differently than naltrexone.[5]
Because it is a quaternary ammonium cation, it cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, and so has antagonist effects throughout the body, counteracting effects such as itching and constipation, but without affecting opioid effects in the brain such as pain relief.[6] However, since a significant fraction (up to 60%) of opioid analgesia can be mediated by opioid receptors on peripheral sensory neurons, particularly in inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, traumatic or surgical pain,[7] MNTX may increase pain under such circumstances.
History
In 1978, a dying friend and colleague presented the late University of Chicago pharmacologist Leon Goldberg with a clinical challenge.[8] Struggling with the pain of prostatic cancer that had metastasized to his bones, the man was now declining the morphine he required for analgesia because of constipation. Research on opioids which would target only the sub-types of receptors associated with pain relief and not with side effects had seen little success outside of in-vitro models. Considering drugs such as loperamide, which acted on the opioid receptors in the gut without acting on the central nervous system, Goldberg proposed a targeted opioid receptor antagonist.[9]
Thousands of opioid-like molecules had been synthesized by pharmaceutical companies looking for the better analgesic - and many of those with no pain-relieving properties had been shelved. Screening these compounds led to the examination of putative antagonists which when modified had properties that suggested they might not readily cross the blood–brain barrier based on their size and charge. One of these compounds, N-methyl-naltrexone (MNTX), was amongst a group of compounds synthesized by Boehringer Ingelheim.[10] The compound looked promising and passed initial screening in which rodents were given opioids along with charcoal meals to track GI transit, and were tested for analgesia.[11] In a 1982 paper by Russell et al., it was first reported that the GI effects of the opioids could be prevented without affecting centrally mediated analgesia in this model.[12] Subsequent preclinical studies also demonstrated this separation of central and peripherally mediated opioid effects for other smooth muscles of the GI tract and the cough reflex.[13][14] Interest also developed in the potential for MNTX to act at the chemoreceptor trigger zone and block the emetic effect of opioids. This blockade of opioid-induced emesis was demonstrated in a canine model.[15][16] Goldberg died before he could see the core of this idea come into clinical practice.
Research on methylnaltrexone continued in the Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care at the University of Chicago through the 1990s. More recent investigations, however, discovered opioid receptors on peripheral sensory neurons.[17] Since inflammatory pain is blunted by endogenous opioid peptides activating such peripheral opioid receptors,[18] MNTX may increase pain under such circumstances.
In December 2005, Wyeth and Progenics entered into an exclusive, worldwide agreement for the joint development and commercialization of methylnaltrexone for the treatment of opioid-induced side effects, including constipation and post-operative ileus (POI), a prolonged dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract following surgery. Under the terms of the agreement, the companies are collaborating on worldwide development. Wyeth received worldwide rights to commercialize methylnaltrexone, and Progenics retained an option to co-promote the product in the United States. Wyeth will pay Progenics royalties on worldwide sales and co-promotion fees within the United States.
Methylnaltrexone is being developed in subcutaneous and oral forms to treat opioid induced constipation (OIC).
The use of methylnaltrexone (Relistor) for more than 4 months has not been studied.[19]
Society and culture
Approval
On April 1, 2008, Progenics and Wyeth announced that Health Canada has approved methylnaltrexone for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation.[20] It was later approved by the US FDA on April 24, 2008.[21][22]
Forms
As of 2010, methylnaltrexone is supplied as an injection in trays containing seven one-dose vials containing 0.6 mL of solution. Each tray also contains seven 12 mm (0.47 in) 1 mL 27 gauge needles with retractable tips, and alcohol wipes for home use. A single vial can treat someone who weighs as much as 115 kilograms (254 lb).[5] For hospital use, vials are available separately.
See also
- Loperamide - an μ-opioid receptor agonist that doesn't cross the BBB in significant amounts, and treats diarrhea (in contrast to methynaltrexone, a Mu-opioid receptor antagonist that doesn't cross the BBB, avoiding opiate withdrawal effects in patients, while treating constipation)
- Naloxegol (trade names Movantik and Moventig) - another peripherally selective opioid antagonist used to treat opioid-induced constipation
- (+)-Naloxone - a non-opioid drug which also reduces some side effects of opioids without significantly affecting analgesia when used in small oral doses
- 6β-Naltrexol (6α-hydroxynaltrexone) - another naltrexone derivative that is also a peripherally selective opioid antagonist
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 70. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Methylnaltrexone Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 21 January 2021. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- 1 2 "Methylnaltrexone (Relistor) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 9 July 2020. Archived from the original on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2020.
- ↑ "Relistor Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- 1 2 "Relistor Full Prescribing Information". Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ↑ National Prescribing Service (1 March 2010). "Methylnaltrexone injections (Relistor) for opioid-induced constipation in palliative care". Archived from the original on 2010-06-01. Retrieved 12 March 2010.
- ↑ Stein C, Lang LJ (2009) Peripheral mechanisms of opioid analgesia. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9(1): 3-8. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2008.12.009.
- ↑ "Drug developed at the University of Chicago wins FDA approval". University of Chicago News. Archived from the original on 2019-08-15. Retrieved 2019-08-15.
- ↑ Moss J (January 2019). "Identifying and Treating Opioid Side Effects: The Development of Methylnaltrexone". Anesthesiology. 130 (1): 142–148. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000002428. PMID 30277930. S2CID 52908307. Archived from the original on 2020-08-10. Retrieved 2021-10-24.
- ↑ US patent 3101339, Karl Zeile and Kurt Freter & Freter, Kurt, "Quaternary salts of normorphine and its acylated derivatives", issued 1963-08-20, assigned to C. H. Boehringer Sohn. About Karl Zeile: born 1905. Untersuchungen über häminhaltige Fermente, habilitation treatise, Technische Hochschule, Munich 1933; In 1933 also SS-Member; 1937 NSDAP-Member; ao. (i.e. extra-ordinary) Professor in Göttingen; 1938 Delegate of NS-Dozentenbund; 1942 Prof. Organic Chemistry and biochemistry at Reichsuniversität Straßburg, and military research; after WW II deputy of Science-Dptm at Chemische Fabrik C. H. Boehringer Ingelheim
- ↑ US patent 4176186, Leon Goldberg, Herbert Merz and Klaus Stockhaus; Merz, Herbert & Stockhaus, Klaus, "Quaternary derivatives of noroxymorphone which relieve intestinal immobility", issued 1979-11-27, assigned to Boehringer Ingelheim
- ↑ Russell J, Bass P, Goldberg LI, Schuster CR, Merz H (March 1982). "Antagonism of gut, but not central effects of morphine with quaternary narcotic antagonists". European Journal of Pharmacology. 78 (3): 255–61. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(82)90026-7. PMID 7200037.
- ↑ Yuan CS, Foss JF, Moss J (March 1995). "Effects of methylnaltrexone on morphine-induced inhibition of contraction in isolated guinea-pig ileum and human intestine". European Journal of Pharmacology. 276 (1–2): 107–11. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(95)00018-G. PMID 7781680.
- ↑ Foss JF, Orelind E, Goldberg LI (1996). "Effects of methylnaltrexone on morphine-induced cough suppression in guinea pigs". Life Sciences. 59 (15): PL235-8. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(96)00451-1. PMID 8845013.
- ↑ Foss JF, Bass AS, Goldberg LI (August 1993). "Dose-related antagonism of the emetic effect of morphine by methylnaltrexone in dogs". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 33 (8): 747–51. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1993.tb05618.x. PMID 8408737. S2CID 217261.
- ↑ US patent 4719215, Leon I. Goldberg, "Quaternary derivatives of noroxymorphone which relieve nausea and emesis", issued 1988-01-12, assigned to University of Chicago
- ↑ Stein C, Schäfer M, Machelska H (2003) Attacking pain at its source: new perspectives on opioids. Nature Med;9(8):1003-1008. doi:10.1038/nm908.
- ↑ Busch-Dienstfertig M, Stein C (2010) Opioid receptors and opioid peptide-producing leukocytes in inflammatory pain-basic and therapeutic aspects. Brain Behav. Immun. 24(5):683-694. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2009.10.013.
- ↑ "Relistor Dosage and Administration". Wyeth. Archived from the original on 2010-08-04. Retrieved 2010-08-12.
- ↑ "Wyeth press release - Wyeth and Progenics Announce Relistor Receives Canadian Marketing Approval". Archived from the original on 2008-04-11. Retrieved 2008-04-01.
- ↑ "Wyeth press release - Progenics and Wyeth Announce FDA has Approved Relistor". Archived from the original on 2008-05-02. Retrieved 2008-04-27.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Relistor for Opioid-Induced Constipation". Archived from the original on 2009-05-13. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
External links
- Holzer P (February 2007). "Treatment of opioid-induced gut dysfunction". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 16 (2): 181–94. doi:10.1517/13543784.16.2.181. PMID 17243938. S2CID 9838569.
- Yuan CS, Foss JF (September 2000). "Oral methylnaltrexone for opioid-induced constipation". JAMA. 284 (11): 1383–4. doi:10.1001/jama.284.11.1383. PMID 10989399.
| Identifiers: |
|---|