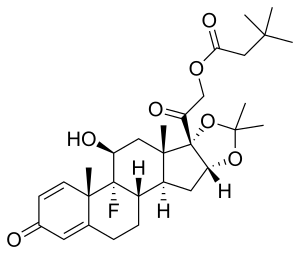
Triamcinolone hexacetonide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Aristospan, Hexatrione, others |
| Other names | Triamcinolone acetonide 21-tebutate; Triamcinolone acetonide 21-(tert-butylacetate); 9α-Fluoro-11β,16α,17α,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with acetone, 21-(3,3-dimethylbutyrate); 9α-Fluoro-11β-hydroxy-16α,17α-((1-methylethylidene)bis(oxy))pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 21-(3,3-dimethylbutyrate) |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Corticosteroid; glucocorticoid |
| Main uses | Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)[1] |
| Side effects | Anxiety, swelling, increased risk of infection, trouble sleeping, peptic ulcer disease[2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Routes of use | Injection into a joint[1] |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H41FO7 |
| Molar mass | 532.649 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Triamcinolone hexacetonide, sold under the brand name Aristospan among others, is a medication used to treat juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).[1] It may also be used for gout, bursitis, and tendinitis.[3] It is given by injection into a joint.[1] Effects last for up to 4 weeks.[4] Triamcinolone acetonide may be used as an alternative.[5]
Side effects may include anxiety, swelling, increased risk of infection, trouble sleeping, and peptic ulcer disease.[2] Rare side effect may include tendon rupture and central serous chorioretinopathy.[2] It is primarily a glucocorticoid with little mineralcorticoid effects.[2]
was approved for medical use in the United States in 1969.[6] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[5] In the United Kingdom a 20 mg vial costs the NHS about £12 as of 2023.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "eEML - Electronic Essential Medicines List". list.essentialmeds.org. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 "Triamcinolone hexacetonide". BNF. Archived from the original on 13 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ↑ "Aristospan®(Triamcinolone Hexacetonide Injectable Suspension, USP)20 mg/mL PARENTERAL". FDA. Archived from the original on 13 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ↑ Lemke, Thomas L. (2008). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 892. ISBN 9780781768795. Archived from the original on 13 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- 1 2 World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ↑ "Aristospan (Injection)". Archived from the original on 19 August 2022. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ↑ "Triamcinolone hexacetonide Medicinal forms". BNF. Archived from the original on 13 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|