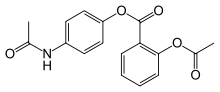
Benorilate
Benorilate (INN), or benorylate, is an ester-linked codrug of aspirin with paracetamol. It is used as an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic medication. In the treatment of childhood fever, it has been shown to be inferior to paracetamol and aspirin taken separately. In addition, because it is converted to aspirin, benorylate is not recommended in children due to concerns about Reye syndrome.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.340 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H15NO5 |
| Molar mass | 313.309 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
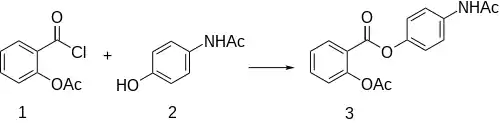
Synthesis
Acetyl salicoyl chloride [5538-51-2] (1) is reacted with paracetamol (2) to give benorilate (3).
Saponification of the ester led to Acetaminosalol (Phenetsal) [118-57-0].[5]
References
- Similä S, Keinänen S, Kouvalainen K (December 1975). "Oral antipyretic therapy: evaluation of benorylate, an ester of acetylsalicylic acid and paracetamol". European Journal of Pediatrics. 121 (1): 15–20. doi:10.1007/bf00464391. PMID 2478. S2CID 21112438.
- NL6504517 idem Andrew Robertson, U.S. Patent 3,431,293 (1969 to Sterling Drug Inc).
- Mario Portelli & Giorgio Renzi, DE 2402231 (1974 to Whitefin Holding SA).
- Huang Xiaocheng, et al. CN 111056968 (2020 to Guangxi University of Science and Technology).
- Moerk Nielsen, N., Bundgaard, H. (March 1989). "Evaluation of glycolamide esters and various other esters of aspirin as true aspirin prodrugs". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 32 (3): 727–734. doi:10.1021/jm00123a040.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.