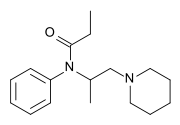
Phenampromide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.517 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H26N2O |
| Molar mass | 274.408 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Phenampromide is an opioid analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs, related to other drugs such as propiram and diampromide. It was invented in the 1960s[1] by American Cyanamid Co.[2] Although never given a general release, it was trialled and 50mg codeine ≈ 60mg phenampromide. Tests on the 2 isomers showed that all of the analgesic effects were caused by the (S) isomer. In the book[3] a 4-phenyl group added to the piperidine-ring produces a drug some x60 morphine.[4] The potency derives from the fact that it overlays fentanyl. Like fentanyl, the addition of a 4-hydroxy group to the 4-piperidylphenyl derivative increases potency to x150 morphine for the racemic compound[5]
Phenampromide produces similar effects to other opioids, including analgesia, sedation, dizziness and nausea.
Phenampromide is in Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act 1970 of the United States as a Narcotic with ACSCN 9638 with a zero aggregate manufacturing quota as of 2014. The free base conversion ratio for salts includes 0.88 for the hydrochloride.[6] It is listed under the Single Convention for the Control of Narcotic Substances 1961 and is controlled in most countries in the same fashion as is morphine.
References
- ↑ Portoghese PS (March 1965). "Stereochemical Studies on Medicinal Agents II. Absolute Configuration of (-)-Phenampromide". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 8: 147–50. doi:10.1021/jm00326a001. PMID 14332652.
- ↑ US 3016382, "N-substituted anilides and method of preparing the same"
- ↑ Lenz GR, Evans SM, Walters DE, Hopfinger AJ (1986). Opiates. Orlando: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-443830-9.
- ↑ US 3518274, "Phenyl substituted n-(2-aminoethyl)-n-benzylamides"
- ↑ 'Opiate Analgesics - Chemistry and receptors' page 470.
- ↑ "Quotas - 2014". Diversion Control Division. Drug Enforcement Agency, U.S. Department of Justice.