I
 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
See also
- (Latin script): Aa Bb Cc Dd Ee Ff Gg Hh Ii Jj Kk Ll Mm Nn Oo Pp Qq Rr Sſs Tt Uu Vv Ww Xx Yy Zz
- (Variations of letter I): Íí Ìì Ĭĭ Îî Ǐǐ Ïï Ḯḯ Ĩĩ Įį Īī Ỉỉ Ȉȉ Ȋȋ Ịị Ḭḭ Ɨɨɨ̆ ᵻ ᶖ İi Iı ɪ Ii fi ffi IJij IJij
- (Letters using dot sign): Ȧȧ Ạạ Ặặ Ậậ Ǡǡ Ḃḃ Ḅḅ Ċċ Ḋḋ Ḍḍ Ėė Ẹẹ Ḟḟ Ġġ Ḣḣ Ḥḥ Ii İi Iı Ịị Ḳḳ Ḷḷ Ṁṁ Ṃṃ Ṅṅ Ṇṇ Ȯȯ Ọọ Ợợ Ṗṗ Ṙṙ Ṛṛ Ṡṡ Ṣṣ ẛ Ṫṫ Ṭṭ Ụụ Ựự Ṿṿ Ẇẇ Ẉẉ Ẋẋ Ẏẏ Ỵỵ Żż Ẓẓ
Symbol
I
- (chemistry) Symbol for iodine.
- (physics) Isotopic spin.
- (license plate codes) Italy
- (physics, electronics) Electrical current.
- (physics, kinematics) moment of inertia.
- (biochemistry) IUPAC 1-letter abbreviation for isoleucine
- (mathematics, linear algebra) identity matrix
- (mathematical analysis, topology) the (closed) unit interval; [0, 1]
- (inorganic chemistry) Specifying an oxidation state of 1
- (music) major tonic triad
Numeral
I (upper case Roman numeral, lower case i)
Gallery
- Letter styles
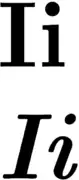 Normal and italic I
Normal and italic I Uppercase and lowercase I in Fraktur
Uppercase and lowercase I in Fraktur
See also
Other representations of I:
References
- “I” in The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, 4th edition, Boston, Mass.: Houghton Mifflin, 2000, →ISBN.
- “I” in Dictionary.com Unabridged, Dictionary.com, LLC, 1995–present.
English
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /aɪ/
- (Southern American English): IPA(key): /aː/
Audio (US) (file) - Rhymes: -aɪ
- Homophones: eye, aye, ay
Etymology 1
From Middle English I ( also ik, ich), from Old English ih ( also ic, iċċ (“I”)), from Proto-Germanic *ik, *ek (“I”), from Proto-Indo-European *éǵh₂ (“I”). Cognate with Scots I, ik, A (“I”), Saterland Frisian iek (“I”), West Frisian ik (“I”), Dutch ik (“I”), Low German ik (“I”), German ich (“I”), Bavarian i (“I”), Danish and Norwegian Bokmål jeg (“I”), Norwegian Nynorsk eg (“I”), Swedish jag (“I”), Icelandic ég, eg (“I”), Latin ego (“I”), Ancient Greek ἐγώ (egṓ, “I”), Russian я (ja, “I”), Lithuanian aš (“I”). See also English ich.
Pronoun
I (first person singular subject personal pronoun, objective me, possessive my, possessive pronoun mine, reflexive myself)
- The speaker or writer, referred to as the grammatical subject, of a sentence.
- 1590, Edmund Spenser, The Faerie Queene, III.ii:
- It ill beseemes a knight of gentle sort, / Such as ye haue him boasted, to beguile / A simple mayd, and worke so haynous tort, / In shame of knighthood, as I largely can report.
- 1854, Gustave Chouquet, Easy Conversations in French, page 9:
- Here I am, sir.
Audio (file)
- 2016, VOA Learning English (public domain)
- I know I have a pen, though…
Audio (US) (file)
- I know I have a pen, though…
- 1590, Edmund Spenser, The Faerie Queene, III.ii:
- (nonstandard, hypercorrection) The speaker or writer, referred to as the grammatical object, of a sentence.
Usage notes
- The word I is always capitalised in written English. Other forms of the pronoun, such as me and my, follow regular English capitalisation rules.
- I is the subject (nominative) form, as opposed to me, which is the objective (accusative and dative) form. Me is also used emphatically, like French moi. In some cases there are differing views about which is preferred. For example, the traditional rule followed by some speakers is to use I as the complement of the copula (It is I), but it is now more usual to choose me in this context (It's me).
- When used in lists, it is often thought more polite to refer to self last. Thus it is more natural to say John and I than I and John. In such lists, we generally use the same case form which we would choose if there were only one pronoun; since we say I am happy, we say John and I are happy, but we say Jenny saw me, so we say Jenny saw John and me. However, colloquially one might hear John and me are happy, which is traditionally seen as a case error. As a hypercorrected reaction to this, one can occasionally hear phrases like Jenny saw John and I.
Derived terms
Translations
See also
| personal pronoun | possessive pronoun | possessive determiner | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| subjective | objective | reflexive | |||||
| first person | singular | I | me | myself | mine | my mine (before vowels, archaic) | |
| plural | we | us | ourselves ourself | ours | our | ||
| second person | singular | standard | you | you | yourself | yours yourn (obsolete outside dialects) | your |
| archaic, informal | thou | thee | thyself theeself | thine | thy thine (before vowels) | ||
| plural | standard | you you all ye (archaic) | you you all | yourselves | yours yourn (obsolete outside dialects) | your | |
| informal / dialectal | (see list of dialectal forms at you and inflected forms in those entries) | ||||||
| third person | singular | masculine | he | him | himself hisself (archaic) | his hisn (obsolete outside dialects) | his |
| feminine | she | her | herself | hers hern (obsolete outside dialects) | her | ||
| neuter | it | it | itself | its his (archaic) | its his (archaic) | ||
| genderless | they | them | themself, themselves | theirs | their | ||
| genderless, nonspecific (formal) |
one | one | oneself | – | one's | ||
| plural | they | them | themselves | theirs theirn (obsolete outside dialects) | their | ||
Etymology 2
- Old French i, from Latin ī, from Etruscan I (i).
Letter
See also
Number
I (upper case, lower case i)
Etymology 3
Abbreviation.
Noun
I (countable and uncountable, plural Is)
- (US, roadway) Interstate.
- (grammar) Abbreviation of instrumental case.
References
- “I” in The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, 4th edition, Boston, Mass.: Houghton Mifflin, 2000, →ISBN.
- “I” in Dictionary.com Unabridged, Dictionary.com, LLC, 1995–present.
- "I" in WordNet 2.0, Princeton University, 2003.
Afar
American Sign Language
Azerbaijani
Letter
I upper case (lower case ı)
Danish
Etymology
From Old Norse ír, variant of ér, from Proto-Germanic *jūz, from Proto-Indo-European *yū́.
Pronoun
I (objective jer, possessive jeres)
- (personal) you, you all (second person plural)
- I må ikke gå derind!
- You can't go in there!
- 2014, Diverse forfattere, Fire uger blev til fire år - og andre beretninger, Lindhardt og Ringhof →ISBN
- Og så er der forresten lidt mere med det samme: I må love os een ting. mor og far, I må ikke efterligne os unge! — For gør I det, ja, så kommer I til at se så morsomme ud. — I må ikke prøve på at løbe fra jeres alder, for det kan I alligevel ikke.
- And by the way, there's something else: You must promise us one thing, mum and dad, you may not imitate us young! — For if you do, you will look so funny. — you may not try to run way from your age, for you can't do that anyway.
- 1981, Mogens Wolstrup, Vild hyben: danske forfattere skriver om jalousi
- Men det er ikke jeres skyld, siger Ditte. I er unge og kloge. I er grimme og fantastisk smukke. I har modet! I er på rette vej med jeres show. Jeg føler med jeres oprør, og måske derfor kunne jeg ikke klare mere. Jeres hud er glat, I er startet i tide.
- But it is not your fault, Ditte says. You are young and intelligent. You are ugly and amazingly beautiful. You have the courage! You are on the right path with your show. I feel with your rebellion, and perhaps for that reason, I couldn't take any more. Your skin is smooth, you started in time.
- Men det er ikke jeres skyld, siger Ditte. I er unge og kloge. I er grimme og fantastisk smukke. I har modet! I er på rette vej med jeres show. Jeg føler med jeres oprør, og måske derfor kunne jeg ikke klare mere. Jeres hud er glat, I er startet i tide.
- 2011, Per Ullidtz, Absalons Europa, BoD – Books on Demand →ISBN, page 229
- Og lidt senere ”I har hørt at det er sagt: øje for øje og tand for tand. Men jeg siger jer, at I må ikke sætte jer imod det onde; men dersom nogen giver dig et slag på din højre kind, da vend ham også den anden til! ...
- And a little later ”you have heard it said: an eye for an eye and a tooth for a tooth. But I say to you, you may not resist evil; but if anyone hits you on the right cheek, turn the other towards [whoever hit you]! ...
- Og lidt senere ”I har hørt at det er sagt: øje for øje og tand for tand. Men jeg siger jer, at I må ikke sætte jer imod det onde; men dersom nogen giver dig et slag på din højre kind, da vend ham også den anden til! ...
See also
| Number | Person | Inflection | Nominative | Accusative | Possessive | Reflexive | Reflexive possessive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | First | common | jeg | mig | min | ||
| neuter | mit | ||||||
| plural | mine | ||||||
| Second | common | du | dig | din | |||
| neuter | dit | ||||||
| plural | dine | ||||||
| formal | De | Dem | Deres | ||||
| Third | masculine | han | ham | hans | sig | sin | |
| feminine | hun | hende | hendes | ||||
| common | den | den | dens | ||||
| neuter | det | det | dets | sit | |||
| plural | sine | ||||||
| Plural | First | — | vi | os | vores | ||
| common | vor | ||||||
| neuter | vort | ||||||
| plural | vore | ||||||
| Second | – | I | jer | jeres | |||
| formal | De | Dem | Deres | ||||
| Third | – | de | dem | deres | sig | ||
Dutch
Pronunciation
- (letter name): IPA(key): /i/
Audio (file)
Esperanto
Letter
I (upper case, lower case i)
German
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /ʔiː/
Related terms
- I longa f
Ido
Italian
Pronunciation
- (phoneme; name of letter) IPA(key): /i/
- (phoneme, when followed by a vowel in the same syllable) IPA(key): /j/
Letter
I m or f (invariable lower case, i)
Latvian
Etymology
Proposed in 1908 as part of the new Latvian spelling by the scientific commission headed by K. Mīlenbahs, which was accepted and began to be taught in schools in 1909. Prior to that, Latvian had been written in German Fraktur, and sporadically in Cyrillic.
Malay
Pronunciation
Middle English
Alternative forms
Etymology
From Old English iċ, from Proto-Germanic *ek, *ik, from Proto-Indo-European *éǵh₂. More at English I.
Pronoun
I (accusative me, genitive min, genitive determiner mi, min)
- I (first-person singular subject pronoun)
References
- “ich (pron.)” in MED Online, Ann Arbor, Mich.: University of Michigan, 2007, retrieved 2018-04-05.
Norwegian Bokmål
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /iː/
Portuguese
Letter
I (upper case, lower case i)
Romanian
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /i/
Usage notes
- Generally represents the phoneme /i/. Preceded by H and followed by Î.
- Before vowels, this letter usually takes on the sound of /j/
- ianuarie /ja.nuˈa.ri.e/
- At the ends of words (except verb infinitives, and those ending in a consonant cluster ending in l or r), the letter palatalizes the previous syllable and is "whispered": /ʲ/
- băieți /bəˈjetsʲ/
Saanich
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /i/
Scots
Etymology 1
From Old English iċ, from Proto-Germanic *ek, *ik, from Proto-Indo-European *éǵh₂.
Slovene
Spanish
Abbreviation
I
- Ilustre
- La I municipalidad de Valparaíso.
Swedish
Etymology
From Old Swedish ī, īr, from Old Norse ír, variant of ér, from Proto-Germanic *jīz, variant of *jūz, from Proto-Indo-European *yū́.
Pronunciation
- Rhymes: -iː
Turkish
Letter
I (upper case, lower case ı)
Vietnamese
Pronunciation
- (Hà Nội) IPA(key): [ʔi˧˧], [ʔi˧˧ ŋan˧˦]
- (Huế) IPA(key): [ʔɪj˧˧], [ʔɪj˧˧ ŋaŋ˦˧˥]
- (Hồ Chí Minh City) IPA(key): [ʔɪj˧˧], [ʔɪj˧˧ ŋaŋ˦˥]
- Phonetic: i, i ngắn
Letter
I (upper case, lower case i)
See also
- (Quốc ngữ letters) chữ; A a (À à, Ả ả, Ã ã, Á á, Ạ ạ), Ă ă (Ằ ằ, Ẳ ẳ, Ẵ ẵ, Ắ ắ, Ặ ặ), Â â (Ầ ầ, Ẩ ẩ, Ẫ ẫ, Ấ ấ, Ậ ậ), B b, C c (Ch ch), D d, Đ đ, E e (È è, Ẻ ẻ, Ẽ ẽ, É é, Ẹ ẹ), Ê ê (Ề ề, Ể ể, Ễ ễ, Ế ế, Ệ ệ), G g (Gh gh, Gi gi), H h, I i (Ì ì, Ỉ ỉ, Ĩ ĩ, Í í, Ị ị), K k (Kh kh), L l, M m, N n (Ng ng, Ngh ngh, Nh nh), O o (Ò ò, Ỏ ỏ, Õ õ, Ó ó, Ọ ọ), Ô ô (Ồ ồ, Ổ ổ, Ỗ ỗ, Ố ố, Ộ ộ), Ơ ơ (Ờ ờ, Ở ở, Ỡ ỡ, Ớ ớ, Ợ ợ), P p (Ph ph), Q q (Qu qu), R r, S s, T t (Th th, Tr tr), U u (Ù ù, Ủ ủ, Ũ ũ, Ú ú, Ụ ụ), Ư ư (Ừ ừ, Ử ử, Ữ ữ, Ứ ứ, Ự ự), V v, X x, Y y (Ỳ ỳ, Ỷ ỷ, Ỹ ỹ, Ý ý, Ỵ ỵ)
Zulu
Letter
I (upper case, lower case i)