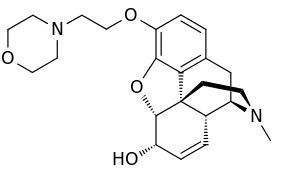
Pholcodine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Logicin and many others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Dependence liability | Low |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Maximum plasma conc. attained 4-8 hours after oral dose. |
| Protein binding | 23.5% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 32-43 hours; volume of distribution is 36-49L/kg. |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.367 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H30N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 398.503 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Pholcodine is a drug which is an opioid cough suppressant (antitussive). It helps suppress unproductive coughs and also has a mild sedative effect, but has little or no analgesic effects. It is also known as morpholinylethylmorphine and homocodeine.
Pholcodine is found in certain cough lozenges,[1] and more commonly as an oral solution, typically 5 mg / 5 ml. Adult dosage is 5-10 ml up to 3-4 times daily.[2] Pholcodine now largely replaces the previously more common codeine linctus, as it has a much lower potential for dependence.
Pholcodine is used as an antitussive agent in Australia, Belgium, Finland, France, Ireland, New Zealand, Norway, and the UK . It is a class B substance in the United Kingdom but can be purchased over-the-counter in most UK pharmacies.[3][4] Pholcodine is not prescribed in the United States where it is classed as a Schedule I drug, the most highly controlled drug category, which includes the likes of heroin, LSD and ecstasy.[5]
Mechanism of action
Pholcodine is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and freely crosses the blood–brain barrier. It acts primarily on the central nervous system (CNS), causing depression of the cough reflex, partly by a direct effect on the cough centre in the medulla. It is metabolized in the liver and its action may be prolonged in individuals with hepatic insufficiency (i.e. liver problems). Its use is therefore contraindicated in patients with liver disease, while care is advised in patients with hepatic impairment.
Metabolism and excretion
Pholcodine is slowly biotransformed in the body via oxidation and conjugation to a series of metabolites that are eliminated primarily in the urine. With an average half-life of approximately 2.3 days, steady-state in someone taking the drug chronically would not be reached for nearly 2 weeks. Nearly one-half of a single dose is eventually excreted as free or conjugated parent drug. The most important urinary metabolite is conjugated morphine, which may be detectable for days or weeks after the last dose. This could trigger a positive result for opiates in a urine drug testing program.[6][7]
Side effects
Side effects are rare and may include dizziness and gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea or vomiting. Adverse effects such as constipation, drowsiness, excitation, ataxia and respiratory depression have been reported occasionally or after large doses. The primary safety concerns with pholcodine revolve around death during general anaesthesia.[8]
Anaphylaxis during general anaesthesia
Administration of pholcodine causes production of antibodies linked with fatalities during surgery, when essential neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs) are administered to prevent patient movement under general anaesthesia.[9] These antibody levels gradually fall to low levels several years after last dose of pholcodine. However, the presence of these antibodies causes a 300-fold increase in risk of anaphylaxis during anaesthesia.[10]
The link was suspected when neighbouring Norway and Sweden were found to have tenfold differences of surgical anaphylaxis deaths. Sweden had no products approved containing pholcodine, whereas 40% of the population in Norway had consumed the single approved pholcodine product.[10] Norway withdrew pholcodine from the market in 2007, and the prevalence of anti-suxamethonium antibodies fell by over 80% in two years.[11] A corresponding fall in anaesthesia deaths followed.[10]
A similar disparity exists between NMBA anaphylaxis rates in Australia, where pholcodine consumption is high and the US, where pholcodine is banned.[12] In the US, anaphylaxis rates are so low that some anaesthetists question the existence of such reactions to NMBAs.[13] Conversely, Australian anaesthetists have requested a ban on pholcodine[14] due to the high anaphylaxis rate in the country.[15] However, the Therapeutic Goods Administration declined the request in January 2015,[16] pending further reviews to follow.
In contrast, the European Medicines Agency's 2012 "Assessment report for Pholcodine containing medicinal products" concludes this: The Committee considered that evidence of an association between pholcodine use and development of NMBA-related anaphylaxis is circumstantial, not entirely consistent and therefore does not support the conclusion that there is a significant risk of cross-sensitisation to NMBAs and subsequent development of anaphylaxis during surgery.[17]
See also
References
- ↑ "Potter's Pholcodine cough pastilles". Lloyds Pharmacy.
- ↑ British National Formulary 54. London: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd., RPS Publishing. 2007. p. 175.
- ↑ "Boots Night Cough Relief". The Boots Company PLC.
- ↑ "Care Pholcodine Linctus". Lloyds Pharmacy.
- ↑ "Legislation - Controlled Substances". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 11 June 2009. Archived from the original on 4 February 2016.
- ↑ Maurer HH, Fritz CF (December 1990). "Toxicological detection of pholcodine and its metabolites in urine and hair using radio immunoassay, fluorescence polarisation immunoassay, enzyme immunoassay, and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry". International Journal of Legal Medicine. 104 (1): 43–6. doi:10.1007/BF01816483. PMID 11453092. S2CID 5935454.
- ↑ Baselt R (2008). Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man (8th ed.). Foster City, CA: Biomedical Publications. pp. 1258–1260.
- ↑ Andalo D (17 January 2015). "Anaesthetists campaign for pholcodine cough medicines to become prescription-only products". The Pharmaceutical Journal. Royal Pharmaceutical Society.
- ↑ Florvaag E, Johansson SG (August 2009). "The pholcodine story". Immunology and Allergy Clinics of North America. 29 (3): 419–27. doi:10.1016/j.iac.2009.04.002. PMID 19563989.
- 1 2 3 Florvaag E, Johansson SG (July 2012). "The Pholcodine Case. Cough Medicines, IgE-Sensitization, and Anaphylaxis: A Devious Connection". The World Allergy Organization Journal. 5 (7): 73–8. doi:10.1097/WOX.0b013e318261eccc. PMC 3651177. PMID 23283141.
- ↑ Florvaag E, Johansson SG, Irgens Å, de Pater GH (July 2011). "IgE-sensitization to the cough suppressant pholcodine and the effects of its withdrawal from the Norwegian market". Allergy. 66 (7): 955–60. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02518.x. PMID 21241314. S2CID 21048759.
- ↑ Sadleir PH, Clarke RC, Bunning DL, Platt PR (June 2013). "Anaphylaxis to neuromuscular blocking drugs: incidence and cross-reactivity in Western Australia from 2002 to 2011". British Journal of Anaesthesia. 110 (6): 981–7. doi:10.1093/bja/aes506. PMID 23335568.
- ↑ Levy JH (April 2004). "Anaphylactic reactions to neuromuscular blocking drugs: are we making the correct diagnosis?". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 98 (4): 881–2. doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000115146.70209.4B. PMID 15041566.
- ↑ Crilly H, Rose M (2014). "Anaphylaxis and anaesthesia–can treating a cough kill?". Australian Prescriber. 37 (3): 74–76. doi:10.18773/austprescr.2014.032.
- ↑ Katelaris CH, Kurosawa M, Moon HB, Borres M, Florvaag E, Johansson SG (April 2014). "Pholcodine consumption and immunoglobulin E-sensitization in atopics from Australia, Korea, and Japan". Asia Pacific Allergy. 4 (2): 86–90. doi:10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.2.86. PMC 4005347. PMID 24809013.
- ↑ Medew J (January 5, 2015). "Cough medicine alert over surgery". The Age.
- ↑ "Assessment report for Pholcodine containing medicinal products" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 17 February 2012.
External links
- Australian Therapeutic Goods Admission document on Pholcodine (Rich Text Format)