α-PCYP
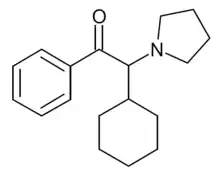
α-PCyP is a stimulant drug of the cathinone class that has been sold online as a designer drug. In a series of alpha-substituted pyrrolidinyl cathinone derivatives developed in 2015, the alpha-cyclopentyl derivative was found to have around the same potency in vitro as an inhibitor of the dopamine transporter as the alpha-propyl derivative α-PVP, while the alpha-cyclohexyl derivative α-PCyP was around twice as strong.[1][2][3]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H25NO |
| Molar mass | 271.404 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
References
- Kolanos R, Sakloth F, Jain AD, Partilla JS, Baumann MH, Glennon RA (October 2015). "Structural Modification of the Designer Stimulant α-Pyrrolidinovalerophenone (α-PVP) Influences Potency at Dopamine Transporters". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 6 (10): 1726–31. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00160. PMC 5349767. PMID 26217965.
- Glennon RA, Dukat M (2016). "Structure-Activity Relationships of Synthetic Cathinones". Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 32: 19–47. doi:10.1007/7854_2016_41. ISBN 978-3-319-52442-9. PMC 5818155. PMID 27830576.
- Baumann MH, Walters HM, Niello M, Sitte HH (2018). "Neuropharmacology of Synthetic Cathinones". Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 252: 113–142. doi:10.1007/164_2018_178. ISBN 978-3-030-10560-0. PMC 7257813. PMID 30406443.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.