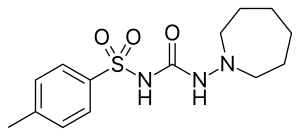
Tolazamide
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tolinase, others |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Sulfonylurea[1] |
| Main uses | Type 2 diabetes[1] |
| Side effects | Nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, low blood sugar[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Onset of action | Within 20 min[1] |
| Duration of action | 10 hrs[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682482 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | metabolized in the liver to active metabolites |
| Elimination half-life | 7 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (85%) and fecal (7%) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H21N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 311.40 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Tolazamide, sold under the brand name Tolinase among others, is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1] Effects begin within 20 minutes and last for about 10 hours.[1]
Common side effects include nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.[1] Other side effects may include rash and low blood sugar.[1] Side effects are more common in people with liver or kidney problems.[1] It is a sulfonylurea.[1]
Tolazamide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1966.[1] It is available as a generic medication.[2] In the United States 90 tablets of 250 mg costs about 54 USD.[3]
Medical uses
Dosage
It is often started at 100 to 250 mg per day with a maximum dose of 1,000 mg per day.[1]
Synthesis
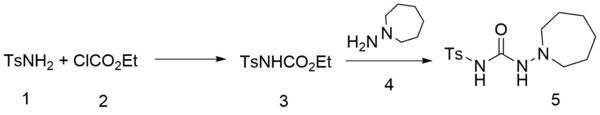
para-Toluenesulfonamide is converted to its carbamate with ethyl chloroformate in the presence of a base. Heating that intermediate with 1-amino-azepane leads to the displacement of the ethoxy group and the formation of tolazemide:[4]
Azepane proper would lead to [13078-23-4].
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "Tolazamide Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 4 September 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ↑ Skyler, Jay (4 April 2012). Atlas of Diabetes. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 186. ISBN 978-1-4614-1027-0. Archived from the original on 9 October 2021. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ↑ "Tolazamide Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- 1 2 Wright JB, Willette RE (July 1962). "Antidiabetic Agents. N4-Arylsulfonylsemicarbazides". Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. 91: 815–22. doi:10.1021/jm01239a016. PMID 14056414.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- "Tolazamide". Medline Plus. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2020-10-19. Retrieved 2020-06-19.