Outline of lichens
The following outline provides an overview of and topical guide to lichens.

Lichen – composite organism made up of multiple species – a fungal partner, one or more photosynthetic partners, which can be either green algae or cyanobacteria, and, in at least 52 genera of lichens, a yeast.[1] In American English, "lichen" is pronounced the same as the verb "liken" (/ˈlaɪkən/). In British English, both this pronunciation and one rhyming with "kitchen" (/ˈlɪtʃən/) are used.[2]
What is a lichen?
A lichen can be described as all of the following:
- Life form – an entity that is alive.
- Composite organism – a symbiotic life form composed of multiple partners from different biological domains, families and kingdoms, and into different phyla, classes and divisions within those domains and kingdoms. In the case of lichens, a fungal partner (the mycobiont) combines with one or more photosynthetic partner(s) (the photobiont) as well as (in some cases) a yeast.
- Eukaryote (domain) – organisms with a cell nucleus within a nuclear envelope; both the mycobiont and any algal partners fall into this domain.[3]
-
- Ascomycota (phylum) and/or Basidiomycota (phylum)[4]
- For the biological classes and families these fungi belong to, see below.
- Chlorophyta (division) – if the photobiont is a green alga, it falls into this taxonomic division.[5]
- Trebouxiophyceae (class)
- Trebouxiaceae (family)[6]
- Ulvophyceae (class)
- Trentepohliaceae (family)[6]
- Prokaryote (domain) – organisms without a cell nucleus; any cyanobacterial partner falls into this domain.[3]
-
- Cyanobacteria (phylum)[7]
Nature of lichens

(a) The cortex is the outer layer of tightly woven fungus filaments (hyphae)
(b) This photobiont layer has photosynthesizing green algae
(c) Loosely packed hyphae in the medulla
(d) A tightly woven lower cortex
(e) Anchoring hyphae called rhizines where the fungus attaches to the substrate
Morphology
- Lichen anatomy and physiology
- Lichen morphology – a lichen's external appearance and structures are very different than those of its individual partners.[8]
- Apoplast – the symbiotic interface zone between the mycobiont and photobiont, outside the cell membranes or walls of both.[9]
- Ascocarp – the fruiting body of a lichen, which contains the asci.[10]
- Cephalodium (PL cephalodia) – a gall-like structure that contains cyanobacteria[15]
- Hypha (PL hyphae) – a long, branching, thread-like structure composed of one or more fungal cells, which typically makes up a large part of lichens; hyphae are densely compacted in the cortex and more loosely interwoven in the medulla.[16]
- Haustorium (PL haustoria) – a root-like structure which allows the fungal partner to extract nutrients from its photosynthetic partner(s).[13]
- Rhizine – a root-like structure that anchors a lichen to the substrate on which it grows.[19]
- Soralium (PL soralia) – a localized region or structure, typically a crack or pore, containing soredium.[20]
- Thallus (PL thalli) – the vegetative body of a lichen, made up of both mycobiont and photobiont components.[21]
- Cortex – the lichen's outer layer(s), made up of tightly woven fungal filaments.[22]
- Isidium (PL isidia) – outgrowths of the thallus which contain photobiont cells and provide means of vegetative reproduction for some lichens.[23]
- Medulla – a loose layer of interwoven fungal hyphae within the thallus[24]
- Podetium (PL podetia) – an upright secondary thallus, which supports the fruiting bodies of Cladonia species.[25]
Ecology

- Symbiosis in lichens – the relationship between the lichen partners can be complicated; while generally mutualistic, sometimes it is not. Recent research also shows other partners, including bacteria and "accessory" fungi, may be involved.[27]
- Asexual reproduction in lichens – many lichens reproduce asexually, using one or more of various methods which allow the dispersal of bundles of both fungal hyphae and photobionts.
- Sexual reproduction in lichens – most lichens reproduce sexually using ascospores, which means they have to acquire their photobiont partners somehow after germinating.[28]
- Lichens and nitrogen cycling – some lichens (in particular those with cyanobacteria as a photobiont) can fix nitrogen.[26]
- Lichen biogeography – the study of the current distribution of extant lichens and the reasons for those distributions.[29]
- Lichen resynthesis – lichens can be artificially "recreated" by combining partners in a lab.[30]
- Lichens and pedogenesis – lichens contribute to the formation of soil by breaking down rock.[31]
- Biological soil crust – lichens are among the common dominant biota in biocrusts, one of the world's largest environmental community types in terms of area covered.[32]
- Photosynthesis in lichens
Types of lichens
Lichen taxonomical classifications
_M%C3%BCll._Arg_237882.jpg.webp)
Lichen systematics – Although they are composite organisms, lichens have traditionally been classified on the basis of their fungal partner. These span eight different biological classes, 39 orders, 117 families, and around 1,000 genera.[33][34]
- Ascolichen – a lichen whose fungal partner is a member of the Ascomycota, one of the two main fungal divisions.[35]
- Basidiolichen – a lichen whose fungal partner is a member of the Basidiomycota, the other of the two main fungal divisions; these are far fewer in occurrence than ascolichens.[36]
Classes
Lichens fall into eight fungal classes and several subclasses:[37]
Orders

They are split across nearly 40 orders. Those which cannot be assigned to a particular order are assigned instead to "incertae sedis" within the appropriate class. These orders were listed in Lücking, Hodkinson and Leavitt's 2016 treatise on the classification of lichenized fungi, except where otherwise noted,[37] with orders updated in 2021.[33]
- Acarosporales
- Agaricales
- Arthoniales
- Atheliales
- Baeomycetales
- Caliciales
- Candelariales
- Cantharellales
- Capnodiales
- Chaetothyriales
- Collemopsidiales
- Coniocybales
- Corticiales
- Eremithallales
- Lecanorales
- Lecideales
- Lepidostromatales
- Leprocaulales
- Lichinales
- Monoblastiales
- Odontotrematales
- Ostropales
- Peltigerales
- Pertusariales
- Phaeomoniellales
- Pleosporales
- Pyrenulales
- Rhizocarpales
- Sarrameanales
- Schaereriales[38][39]
- Strigulales
- Teloschistales
- Thelenellales[38][39]
- Thelocarpales
- Trypetheliales
- Umbilicariales
- Verrucariales
- Vezdaeales
- Xylariales
Families
They fall into 117 families. Those which cannot be assigned to a particular family are assigned instead to "incertae sedis" within the appropriate order. These were listed in Lücking, Hodkinson and Leavitt's 2016 treatise on the classification of lichenized fungi, except where otherwise noted;[34] families were updated in 2021.[33]
- Acarosporaceae
- Agyriaceae
- Andreiomycetaceae
- Aphanopsidaceae
- Arctomiaceae
- Arthoniaceae
- Arthrorhaphidaceae
- Atheliaceae
- Baeomycetaceae
- Biatorellaceae
- Brigantiaeaceae
- Caliciaceae
- Cameroniaceae
- Candelariaceae
- Carbonicolaceae
- Catillariaceae
- Celotheliaceae
- Chrysotrichaceae
- Cladoniaceae
- Clavulinaceae
- Coccocarpiaceae
- Coccotremataceae
- Coenogoniaceae
- Collemataceae
- Coniocybaceae
- Corticiaceae
- Cystocoleaceae
- Dacampiaceae
- Dactylosporaceae
- Elixiaceae
- Fuscideaceae[40]
- Gloeoheppiaceae
- Gomphillaceae
- Graphidaceae
- Gyalectaceae
- Gypsoplacaceae
- Haematommataceae
- Harpidiaceae[41]
- Helocarpaceae
- Hygrophoraceae
- Hymeneliaceae
- Icmadophilaceae
- Koerberiaceae
- Lecanographaceae
- Lecanoraceae
- Lecideaceae
- Lepidostromataceae
- Leprocaulaceae
- Letrouitiaceae
- Lichinaceae
- Lopadiaceae
- Lyrommataceae
- Malmideaceae
- Massalongiaceae
- Megalariaceae
- Megalosporaceae
- Megasporaceae
- Melaspileaceae
- Microtheliopsidaceae
- Monoblastiaceae
- Mycoporaceae
- Nephromataceae
- Ochrolechiaceae
- Opegraphaceae
- Ophioparmaceae
- Pachyascaceae
- Pannariaceae
- Parmeliaceae
- Peltigeraceae
- Peltulaceae
- Pertusariaceae
- Phaneromycetaceae[40][42]
- Phlyctidaceae
- Physciaceae
- Pilocarpaceae
- Placynthiaceae
- Protothelenellaceae
- Psilolechiaceae
- Psoraceae
- Pycnoraceae
- Pyrenotrichaceae
- Pyrenulaceae
- Ramalinaceae
- Ramboldiaceae
- Redonographaceae[40]
- Requienellaceae
- Rhizocarpaceae
- Roccellaceae
- Roccellographaceae
- Ropalosporaceae
- Sagiolechiaceae
- Sarrameanaceae
- Schaereriaceae
- Scoliciosporaceae
- Sphaerophoraceae
- Sporastatiaceae
- Stereocaulaceae
- Stictidaceae
- Strangosporaceae
- Strigulaceae
- Teloschistaceae
- Tenuitholiascaceae[43][44]
- Tephromelataceae
- Thelenellaceae
- Thelocarpaceae
- Thrombiaceae
- Trapeliaceae
- Trichosphaeriaceae[41]
- Trichotheliaceae[40]
- Trypetheliaceae
- Umbilicariaceae
- Vahliellaceae
- Varicellariaceae
- Verrucariaceae
- Vezdaeaceae
- Xanthopyreniaceae
- Xylographaceae
Genera
Extant lichens are found in more than 1000 genera. These were listed in Lücking, Hodkinson and Leavitt's 2016 treatise on the classification of lichenized fungi, except where otherwise noted.[34]
- Absconditella
- Acantholichen
- Acanthothecis
- Acanthotrema
- Acarospora
- Acarosporina
- Aciculopsora
- Acolium
- Acrocordia
- Acroscyphus
- Actinoplaca
- Adelolecia
- Aderkomyces
- Aggregatorygma
- Agonimia
- Ahtiana
- Ainoa
- Albemarlea[45]
- Alectoria
- Allantoparmelia
- Allocalicium
- Allocetraria
- Allographa[46]
- Allophoron[41]
- Alyxoria
- Amandinea
- Amazonomyces
- Amazonotrema
- Ameliella
- Amphorothecium
- Ampliotrema
- Amundsenia
- Amygdalaria
- Amylora
- Anamylopsora
- Anaptychia
- Ancistrosporella
- Andina[47]
- Andreiomyces
- Anema
- Angiactis
- Anisomeridium
- Anomalographis
- Anomomorpha
- Antennulariella
- Anthracocarpon
- Anthracothecium
- Anzia
- Anzina
- Apatoplaca
- Aphanopsis
- Aplanocalenia
- Aptrootia
- Aquacidia[48]
- Architrypethelium
- Arctocetraria
- Arctomia
- Arctoparmelia
- Argopsis
- Aridoplaca[49]
- Arrhenia
- Arthonia (list)
- Arthopyrenia
- Arthotheliopsis
- Arthothelium
- Arthrorhaphis
- Arthrosporum
- Asahinea
- Aspicilia
- Aspiciliopsis
- Aspidothelium
- Aspilidea
- Asteristion
- Asteroporum
- Asterothyrium
- Astrochapsa
- Astrothelium
- Athallia
- Athelopsis
- Atla
- Atrophysma[50]
- Aulaxina
- Auriculora
- Australiaena
- Australidea[51]
- Austrella
- Austrographa
- Austrolecia
- Austromelanelixia[52][53]
- Austroparmelina
- Austropeltum
- Austroplaca
- Austroroccella
- Austrotrema
- Awasthiella
- Bacidia
- Bacidina
- Bacidiopsora
- Bactrospora
- Baculifera
- Badimia
- Badimiella
- Baeomyces
- Baflavia
- Bagliettoa
- Bahianora
- Baidera[54]
- Bapalmuia
- Bartlettiella
- Barubria
- Bathelium
- Bellemerea
- Biatora
- Biatorella
- Biatoridium
- Bibbya[55]
- Bilimbia
- Blastenia
- Blastodesmia
- Blennothallia
- Bogoriella
- Boreoplaca
- Borinquenotrema
- Botryolepraria
- Bouvetiella
- Brasilicia
- Brianaria
- Brigantiaea
- Brodoa
- Brownliella
- Bryobilimbia
- Bryocaulon
- Bryodina
- Bryogomphus
- Bryonora
- Bryoplaca
- Bryoria
- Bryostigma
- Brysstrema
- Buellia (list)
- Buelliastrum
- Bulbothrix
- Bunodophoron
- Burrowsia[56]
- Byssolecania
- Byssoloma
- Caeruleum
- Calathaspis
- Calenia
- Caleniopsis
- Calicium
- Callome
- Calogaya
- Calopadia
- Calopadiopsis
- Caloplaca (list)
- Calotrichopsis
- Calvitimela
- Calycidium
- Cameronia
- Candelaria
- Candelariella
- Candelina
- Canoparmelia
- Caprettia
- Carassea
- Carbacanthographis
- Carbonicola
- Catapyrenium
- Catarrhospora
- Catarraphia
- Catenarina
- Catillaria
- Catillochroma
- Catinaria
- Catolechia
- Cecidonia
- Celothelium
- Cenozosia
- Cephalophysis
- Cerothallia
- Cetradonia
- Cetraria
- Cetrariella
- Cetrelia
- Cetreliopsis
- Chaenotheca
- Chapsa
- Charcotiana
- Cheiromycina
- Chiodecton
- Chirleja
- Chrismofulvea
- Chromatochlamys
- Chroodiscus
- Chrysothrix
- Cinnabaria[57]
- Ciposia
- Circinaria
- Cladia
- Cladidium
- Claurouxia
- Cladonia (list)
- Clandestinotrema
- Clathroporina
- Clauzadea
- Clauzadeana
- Clauzadella
- Clavascidium
- Cliostomum
- Clypeopyrenis
- Coccocarpia
- Coccotrema
- Coelopogon
- Coenogonium
- Collema
- Collemopsidium
- Combea
- Compositrema
- Compsocladium
- Coniangium
- Coniarthonia
- Coniocarpon
- Conotremopsis
- Constrictolumina
- Coppinsia
- Cora
- Corella
- Coronoplectrum
- Cornicularia
- Corticorygma
- Corynecystis
- Coscinocladium
- Cratiria
- Creographa
- Crespoa
- Cresponea
- Cresporhaphis[41]
- Crocellina
- Crocodia
- Crocynia
- Cruentotrema
- Crustospathula
- Crutarndina
- Cryptodictyon
- Cryptodiscus
- Cryptolechia
- Crypthonia
- Cryptophaea
- Cryptothecia
- Cryptothele
- Culbersonia
- Cyanoporina
- Cyphelium
- Cyphellostereum
- Cyphobasidium
- Cystocoleus
- Dacampia
- Dactylina
- Davidgallowaya
- Degelia
- Dendriscosticta
- Dendrographa
- Dermatiscum
- Dermatocarpon
- Dermiscellum
- Diaphorographis
- Dibaeis
- Dichosporidium
- Dictyocatenulata
- Dictyographa
- Dictyomeridium
- Dictyonema
- Digitothyrea
- Dijigiella[58][59]
- Dimelaena
- Dimidiographa
- Diorygma
- Diploicia
- Diploschistella
- Diploschistes
- Diplotomma
- Dirinaria
- Dirina
- Dirinastrum
- Diromma
- Distopyrenis
- Distothelia
- Dolichocarpus
- Dolichousnea[60][53]
- Ducatina[61][62]
- Dufourea
- Dyplolabia
- Echidnocymbium
- Echinoplaca
- Edrudia
- Edwardiella
- Eiglera
- Eilifdahlia
- Elixia
- Elixjohnia[63][59]
- Emmanuelia[64]
- Emodomelanelia
- Encephalographa
- Enchylium
- Endocarpon
- Endocena
- Endohyalina
- Enterodictyon
- Enterographa
- Epilichen
- Enigmotrema
- Eopyrenula
- Ephebe
- Eremastrella
- Eremithallus
- Eremothecella
- Erinacellus
- Erioderma
- Ertzia
- Erythrodecton
- Eschatogonia
- Esslingeriana
- Eugeniella
- Eumitria[60][53]
- Euopsis
- Evernia
- Everniopsis
- Farnoldia
- Fauriea
- Feigeana
- Felipes
- Fellhanera
- Fellhaneropsis
- Ferraroa
- Fibrillithecis
- Filsoniana
- Finkia
- Fissurina
- Flabelloporina[65]
- Flakea
- Flavobathelium
- Flavocetraria
- Flavoparmelia
- Flavoplaca
- Flavopunctelia
- Flegographa
- Fluctua
- Follmannia
- Follmanniella
- Fominiella[66]
- Fouragea
- Franwilsia
- Frigidopyrenia
- Frutidella
- Fulgidea
- Fulvophyton
- Fuscidea
- Fuscoderma
- Fuscopannaria
- Gabura[41]
- Gassicurtia
- Geisleria
- Gibbosporina
- Gintarasia
- Gintarasiella[67]
- Glaucotrema
- Gloeheppia
- Glomerilla
- Glomerulophoron
- Glyphis
- Glypholecia
- Glyphopeltis
- Glyphopsis
- Glysoplaca
- Gomphillus
- Gondwania
- Gorgadesia
- Gossypiothallon
- Gowardia
- Granulopyrenis
- Graphidastra
- Graphis
- Gregorella
- Gudelia
- Gyalecta
- Gyalectaria
- Gyalectidium
- Gyalidea
- Gyalideopsis
- Gyalolechia
- Gymnoderma
- Gymnographa
- Gymnographopsis
- Gyrocollema
- Gyrographa
- Gyronactis
- Gyrotrema
- Haematomma
- Halecania
- Halegrapha
- Halographis
- Haloplaca
- Haplodina
- Haploloma
- Harpidium
- Harusavskia[68]
- Heiomasia
- Helicobolomyces[69][70]
- Helminthocarpon
- Helocarpon
- Hemithecium
- Henrica
- Heppia
- Heppsora
- Herpothallon
- Hertella
- Herteliana
- Hertelidea
- Heterocarpon
- Heterocyphelium
- Heterodermia
- Heteromyces
- Heteroplacidium
- Himantormia
- Hippocrepidea
- Homothecium
- Hormosphaeria
- Hosseusia
- Huea
- Hueidea
- Huneckia
- Hydropunctaria
- Hymenelia
- Hyperphyscia
- Hypocenomyce
- Hypoflavia
- Hypogymnia
- Hypotrachyna
- Icmadophila
- Igneoplaca
- Ikaeria[71]
- Immersaria
- Imshaugia
- Ingaderia
- Ingvariella
- Inoderma
- Involucropyrenium
- Ionaspis
- Ioplaca
- Isalonactis
- Jamesiella
- Japewia
- Japewiella
- Jarmania
- Jasonhuria
- Jenmania
- Joergensenia
- Josefpoeltia
- Julella[41]
- Kaernefeltia
- Kaernefia
- Kalbiana
- Kalbionora[72][73]
- Kalbographa
- Kashiwadia
- Kantvilasia
- Klauskalbia[74]
- Knightiella[41]
- Koerberia
- Koerberiella
- Krogia
- Kroswia
- Kuettlingeria
- Kurokawia[75]
- Labyrintha
- Lambiella
- Lasallia
- Lasioloma
- Lathagrium
- Lazarenkoella
- Lecanactis
- Lecania
- Lecanographa
- Lecanora (list)
- Lecidea (list)
- Lecidella
- Lecidoma
- Lecidopyrenopsis
- Leciophysma
- Leifidium
- Leightoniella
- Leimonis
- Leioderma
- Leiorreuma
- Lemmopsis
- Lempholemma
- Lendemeriella
- Lepidocollema
- Lepidostroma
- Lepra
- Leprantha
- Lepraria
- Leprocaulon
- Leprocollema
- Leproplaca
- Leptochidium
- Leptogidium
- Leptogium
- Leptorhaphis
- Leptotrema
- Letharia
- Lethariella
- Letrouitia
- Leucodecton
- Leucodermia
- Lichenomphalia
- Lichina
- Lichinella
- Lichinodium
- Lignoscripta
- Lithoglypha
- Lithographa
- Lithogyalideopsis
- Lithothelium
- Llimonaea
- Lobaria
- Lobariella
- Lobarina
- Lobothallia
- Loekoesia
- Loflammia
- Loflammiopsis
- Logilvia
- Lopacidia
- Lopadium
- Lopezaria
- Loxospora
- Loxosporopsis
- Lueckingia
- Lyromma
- Magmopsis
- Malcolmiella
- Malmidea
- Malmographina
- Mangoldia
- Marcelaria
- Marchandiomphalina
- Marchantiana
- Marfloraea
- Maronea
- Maronella
- Maronina[60][76]
- Masonhalea
- Massalongia
- Mastodia
- Mawsonia
- Mazaediothecium
- Mazosia
- Megalaria
- Megaloblastenia
- Megalospora
- Megalotremis
- Megaspora
- Melanelia
- Melanelixia
- Melanohalea
- Melanolecia
- Melanophloea
- Melanotopelia
- Melanotrema
- Melarthonis
- Melaspilea
- Menegazzia (list)
- Meridianelia
- Metamelanea
- Metus
- Micarea
- Microtheliopsis
- Milospium
- Miltidea
- Minksia
- Miriquidica
- Mischoblastia
- Mobergia
- Monerolechia
- Monoblastia
- Montanelia
- Moriola
- Multiclava
- Multisporidea[77]
- Mycobilimbia
- Mycoblastus
- Mycoporum
- Myelochroa
- Myeloconis
- Myelorrhiza
- Myriolecis
- Myrionora
- Myriospora
- Myriostigma
- Myochroidea
- Nadvornikia
- Nebularia
- Neocatapyrenium
- Neophyllis
- Neopsoromopsis
- Neosergipea
- Nephroma
- Nephromopsis
- Nevesia
- Niebla
- Nigrovothelium
- Nipponoparmelia
- Nitidochapsa
- Nodobryoria
- Normandina
- Notocladonia
- Notolecidea
- Notoparmelia
- Novomicrothelia
- Nyungwea
- Obscuroplaca[78]
- Ocellomma
- Ocellularia (list)
- Ochrolechia
- Oevstedalia
- Olegblumia
- Oletheriostrigula
- Omphalodium
- Omphalora
- Opegrapha
- Ophioparma
- Orceolina
- Orcularia
- Orientophila
- Oropogon
- Orphniospora
- Oxnerella
- Pachnolepia
- Pachyascus
- Pachypeltis
- Pachyphysis
- Palicella
- Pallidogramme
- Pannaria
- Pannoparmelia
- Parabagliettoa
- Paracollema
- Paragyalideopsis[79][80]
- Paraingaderia
- Parainoa
- Paraporpidia
- Paraschismatomma
- Parasiphula
- Paratopeliopsis
- Paratricharia
- Parmelia
- Parmeliella
- Parmelina
- Parmelinella
- Parmeliopsis
- Parmostictina
- Parmotrema (list)
- Parmotremopsis
- Parvoplaca
- Paulia
- Peccania
- Pectenia
- Peltigera
- Peltula
- Peltularia
- Pentagenella
- Pertusaria (list)
- Petractis
- Phaeographis
- Phaeographopsis
- Phaeophyscia
- Phaeorrhiza
- Phloeopeccania
- Phlyctis
- Phoebus
- Phylliscidium
- Phyllisciella
- Phylliscidiopsis
- Phylliscum
- Phyllobaeis
- Phyllobathelium
- Phylloblastia
- Phyllocratera
- Phyllogyalidea
- Phyllopsora
- Physcia
- Physcidia
- Physciella
- Physconia
- Physma
- Piccolia
- Pilophorus
- Placidiopsis
- Placidium
- Placocarpus
- Placolecis
- Placomaronea
- Placopsis
- Placopyrenium
- Placothelium
- Placynthiella
- Placynthiopsis
- Placynthium
- Platismatia
- Platygramme
- Platythecium
- Plectocarpon
- Pleopsidium
- Pleurosticta
- Pliariona
- Podostictina
- Podotara
- Poeltiaria
- Poeltidea
- Poeltinula
- Polistroma
- Polyblastia
- Polyblastidium
- Polycauliona
- Polychidium
- Polymeridium
- Polypyrenula
- Polysporina
- Porina
- Porocyphus
- Porpidia
- Porpidinia[41]
- Protoblastenia
- Protomicarea
- Protopannaria
- Protoparmelia
- Protoparmeliopsis
- Protoroccella[41]
- Protothelenella
- Protousnea
- Psammina
- Psathyrophlyctis
- Pseudarctomia
- Pseudephebe
- Pseudevernia
- Pseudobaeomyces
- Pseudocalopadia
- Pseudochapsa
- Pseudocyphellaria
- Pseudohepatica
- Pseudoheppia
- Pseudolecanactis
- Pseudoleptogium
- Pseudopannaria
- Pseudoparmelia
- Pseudopaulia
- Pseudopeltula
- Pseudopyrenula
- Pseudoramonia
- Pseudosagedia
- Pseudoschismatomma
- Pseudothelomma
- Pseudotopeliopsis
- Psilolechia
- Psiloparmelia
- Psora
- Psorinia
- Psoroglaena
- Psoroma
- Psoromella
- Psoromidium[41]
- Psoronactis
- Psorotheciopsis
- Psorotichia
- Psorula
- Pterygiopsis
- Ptychographa
- Pulvinodecton
- Pulvinora[81]
- Punctelia
- Punctonora
- Puttea
- Pycnora
- Pycnothelia
- Pycnotrema
- Pyrenocarpon
- Pyrenocollema
- Pyrenodesmia
- Pyrenopsis
- Pyrenothrix
- Pyrenowilmsia
- Pyrenula (list)
- Pyrgillus
- Pyrrhospora
- Pyxine
- Racodium
- Racoleus
- Raesaeneniana
- Ramalea
- Ramalina
- Ramalodium
- Ramboldia
- Ramonia
- Redingeria
- Redonia
- Redonographa
- Reichlingia
- Reimnitzia
- Relicina
- Remototrachyna
- Requienella
- Rhabdodiscus
- Rhabdopsora
- Rhaphidicyrtis
- Rhexophiale
- Rhizocarpon
- Rhizolecia
- Rhizoplaca
- Ricasolia
- Rimularia
- Rinodina (list)
- Rinodinella
- Robergea
- Rocella
- Roccellographa
- Roccellina
- Roccellinastrum
- Rockefellera[82]
- Rolfidium
- Rolueckia
- Romjularia
- Ropalospora
- Rostania
- Rubrotricha
- Rufoplaca
- Rusavskia
- Sagedia
- Sagema
- Sagenidiopsis
- Sagiolechia
- Sanguinotrema
- Santessonia
- Sarcographa
- Sarcographina
- Sarcogyne
- Sarcosagium
- Sarea
- Sarrameana
- Savoronala
- Schadonia
- Schaereria
- Schismatomma
- Schistophoron
- Schizodiscus
- Schizopelte
- Schizotrema
- Schizoxylon
- Sclerococcum
- Sclerophora
- Sclerophyton
- Scleropyrenium
- Scoliciosporum
- Sculptolumina
- Scutaria
- Scytinium
- Sedelnikovaea
- Segestria
- Seirophora
- Semigyalecta
- Semiomphalina
- Septotrapelia
- Servitia
- Shackletonia
- Sigridea
- Simonyella
- Sipmaniella
- Siphula
- Siphulastrum
- Siphulella
- Sipmania
- Sirenophila
- Snippocia[83][70]
- Solenopsora
- Solitaria
- Solorina
- Solorinaria
- Sparria
- Speerschneidera
- Sphaerophorus
- Sphaerophoropsis
- Spheconisca
- Sphinctrinopsis
- Spilonema
- Sporastatia
- Sporodictyon
- Sporodophoron
- Sporopodiopsis
- Sporopodium
- Sporostigma
- Sprucidea[84][76]
- Squamarina
- Squamella
- Squamulea
- Staurospora[85][86]
- Staurolemma
- Staurothele
- Stegobolus
- Steinera
- Steineropsis
- Steinia
- Stellarangia
- Stenhammarella
- Stephanocyclos
- Stereocaulon
- Sticta
- Stictis
- Stigmatochroma
- Stigmidium
- Strangospora
- Streimannia
- Streimanniella
- Stirtonia
- Stirtoniella
- Strigula
- Stromatella
- Sulcaria
- Sulcopyrenula
- Sulzbacheromyces
- Synalissa
- Synarthonia
- Synarthothelium
- Syncesia
- Szczawinskia
- Tania
- Tapellaria
- Tapellariopsis
- Tarasginia
- Tarbertia
- Tasmidella
- Tassiloa
- Tayloriellina
- Teloschistes
- Teloschistopsis
- Tenuitholiascus[87][44]
- Tephromela
- Tetramelas
- Teuvoa
- Texosporium
- Thallinocarpon
- Thalloloma
- Thamnochrolechia
- Thamnolecania
- Thamnolia
- Thecaria
- Thecographa
- Thelenella
- Thelenidia
- Thelidiopsis
- Thelignya
- Thelliana
- Thelocarpon
- Thelomma
- Thelopsis
- Thelotrema
- Thermutis
- Thermutopsis
- Tholurna
- Thrombium
- Thyrea
- Thysanothecium
- Tibellia
- Timdalia
- Tingiopsidium
- Toensbergia
- Toninia
- Toniniopsis
- Topelia
- Topeliopsis
- Tornabea
- Trapelia
- Trapeliopsis
- Traponora
- Tremolecia
- Tremotylium[41]
- Tricharia
- Trichothelium
- Trimmatothele
- Trimmatothelopsis
- Trinathotrema
- Trizodia
- Trypetheliopsis
- Trypethelium
- Tuckermanella
- Tuckermanopsis
- Tylophorella
- Tylophoron
- Tylophoropsis
- Tylothallia
- Umbilicaria
- Usnea
- Usnocetraria
- Usnochroma
- Vahliella
- Vainionora
- Varicellaria
- Variospora
- Verrucaria (list)
- Verruculopsis
- Verseghya[88]
- Vezdaea
- Vigneronia
- Villophora
- Violella
- Viridothelium
- Vulpicida
- Wadeana
- Wahlenbergiella
- Watsoniomyces[89]
- Wawea
- Waynea
- Wetmoreana
- Willeya
- Wirthiotrema
- Xalocoa
- Xanthocarpia
- Xanthomendoza
- Xanthoparmelia (list)
- Xanthopeltis
- Xanthopsorella
- Xanthoria
- Xenolecia
- Xenus
- Xyleborus
- Xylographa
- Xyloschistes
- Xylospora
- Yarrumia
- Yoshimuria
- Yoshimuriella
- Zahlbrucknerella
- Zeroviella
- Zwackhia
Species
In 2009, taxonomists estimated that the total number of lichen species (including those yet undiscovered) might be as high as 28,000.[90] By 2016, 19,387 species of lichens had been described and widely accepted.[91]
Lichens, by growth form

Lichen growth forms – These vary depending on the species:
- Crustose – paint-like appearance that adheres tightly to the underlying substrate.[93]
- Foliose – flattened, leafy appearance.[94]
- Fruticose – shrubby, bush-like or coral-like appearance.[94]
- Byssoid – wispy, with the appearance of teased wool.[96]
- Filamentous – thin, threadlike growth, often with a matted appearance.[97]
- Gelatinous – jelly-like interior, due to presence of cyanobacteria.[98]
- Squamulose – scaly, sometimes leafy appearance; can resemble a foliose lichen but usually has no outer cortex.[99]
- Cladoniform – squamulose, but with fruticose podetia.[100]
Lichens, by substrate

Lichens can be classified by the substrate on which they grow:
- Bryophilous lichen – on mosses or liverworts.[101]
- Hepaticolous lichen – on liverworts.[102]
- Muscicolous lichen – on mosses.[103]
- Corticolous lichen – on bark.[101]
- Ramicolous lichen – on twigs.[103]
- Foliicolous lichen – on plant leaves.[101]
- Epiphyllous lichen – on the upper surface of a leaf.[104]
- Hypophyllous lichen – on the lower surface of a leaf.[104]
- Lichenicolous lichen – on other lichens.[101]
- Lignicolous lichen – on wood stripped of bark.[101]
- Omnicolous lichen – on a variety of substrates.[103]
- Plasticolous lichen – on plastic.[105]
- Saxicolous lichen – on stone.[101]
- Endolithic lichen – within stone.[22]
- Terricolous lichen – on soil.[103]
- Vagrant lichen – loose, on no substrate.[106]
Lichens, by region
Australia
Europe
North America
- List of lichens of Maryland
- List of lichens of Soldiers Delight – lichens of a nature reserve in Maryland
- List of lichen species of Montana
- Lichens of the Sierra Nevada (U.S.)
Photobiont
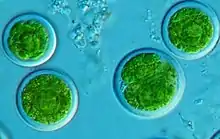
Photobiont – the photosynthetic partner in a lichen.[108]
- Cyanolichen – a lichen with a cyanobacteria photobiont.[109]
- List of lichen photobionts
Lichen metabolites
Lichen product – organic products, known as secondary metabolites, produced by lichens; these provide a variety of protections for the lichen – from microbes, viruses, herbivores, radiation, oxidants and more.[110]
- List of lichen products

Study of lichens
Lichenology – the study of lichens.[112]
- Acharius Medal – awarded for lifetime achievement in lichenology.[113]
- Evolution of lichens – lichenization of fungi has occurred multiple times, and several pathways towards acquiring photobionts have arisen.
- List of fossil lichens
- Exsiccata (plural exsiccatae) – a published set of preserved specimens, numbered and distributed with printed labels.[114]
- History of lichenology
- Lichenometry – a process where measuring the growth of a lichen colony over time can be used to estimate the minimum age of the substrate on which it is growing.[115]
- Spot test (lichen) – chemical tests used to aid in species identification.[116]
Threats
- Lichenicolous fungus – parasitic fungus that uses lichens as a host.[117]
- List of lichenicolous fungi
- Lichens as bioindicators – lichens are sensitive to various pollutants and can be thus be used as bioindicators.[118]
Lichens in culture

- Cultural depictions of lichens
- Trouble with Lichen – science fiction novel by John Wyndham in which lichens play a major role.[122]
- Edible lichen – some lichens have traditionally been used as food.[123]
- Ethnolichenology – a branch of ethnobotany that studies human usage of lichens.[124]
Lichen organizations
- The Bryologist – peer-reviewed journal published by ABLS.
- Australasian Lichen Society
- Australasian Lichenology – official publication of the Australasian Lichen Society.
- British Lichen Society (BLS)
- The Lichenologist – peer-reviewed journal published by the BLS.
- Bryological and Lichenological Association for Central Europe (BLAM)
- Herzogia – peer-reviewed journal published by BLAM.
- Bryological and Lichenological Working Group (Bryologische en Lichenologische Werkgroep, BLWG)
- Buxbaumiella – peer-reviewed journal published by BLWG.
- Dutch Bryological and Lichenological Society
- Lindbergia – peer-reviewed journal co-published by the Dutch Bryological and Lichenological Society and the Nordic Bryological Society.
- Indian Lichenological Society
- International Association for Lichenology (IAL)
- Nordic Bryological Society
Independent lichenological journals
- Asian Journal of Mycology – an international peer-reviewed journal published by Mae Fah Luang University in Thailand.
- Bibliotheca Lichenologica – scientific monographs on lichens and mosses.
- Hattoria – an international, peer-reviewed journal issued by Hattori Botanical Laboratory.
- International Journal of Mycology and Lichenology
See also
Citations
- Van Hoose 2021.
- Cambridge Dictionary.
- Favor 2005, p. 5.
- Laundon 1986, p. 3.
- Li et al. 2021, p. evab101.
- Purvis 2000, p. 9.
- Laundon 1986, p. 2.
- Baron 1999, p. 14.
- Honegger 1998, p. 197.
- Hawksworth, Sutton & Ainsworth 1983, p. 26.
- Silverstein, Silverstein & Silverstein 1996, p. 32.
- Smith et al. 2009, p. 22.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 758.
- Smith et al. 2009, p. 30.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 756.
- Hale 1983, pp. 3, 6.
- Smith et al. 2009, p. 36.
- Smith et al. 2009, p. 24.
- Hawksworth, Sutton & Ainsworth 1983, p. 330.
- Smith et al. 2009, p. 38.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 763.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 757.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 759.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 760.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 761.
- Henriksson & Simu 1971, p. 119.
- Smith et al. 2020, p. 134.
- Bowler & Rundel 1975, p. 326–327.
- Galloway 2012, p. 315.
- Zakeri et al. 2022, p. 80.
- Chen, Blume & Beyer 2000, p. 124.
- Green et al. 2018, p. 397.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022.
- Lücking, Hodkinson & Leavitt 2016, p. 377–400.
- Bendre 2010, p. 131.
- Lepp 2014.
- Lücking, Hodkinson & Leavitt 2016, p. 371.
- Kraichak et al. 2018a.
- Kraichak et al. 2018b.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 162.
- Lücking, Hodkinson & Leavitt 2017, p. 58.
- Gamundí & Spinedi 1985, p. 112.
- Jiang et al. 2020, p. 11.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 124.
- Lendemer, Harris & Ruiz 2016, p. 26.
- Lücking & Kalb 2018, p. 353.
- Wilk et al. 2021, p. 289.
- Aptroot, Sparrius & Alvarado 2018, p. 12.
- Wilk et al. 2021, p. 292.
- Spribille et al. 2020, p. 85.
- Kantvilas, Wedin & Svensson 2021, p. 400.
- Divakar et al. 2017, p. 110.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 150.
- Diederich & Ertz 2020, p. 22.
- Kistenich et al. 2018, p. 871.
- Fryday et al. 2020, p. 473.
- Wilk et al. 2021, p. 293.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2017, p. 79.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 156.
- Divakar et al. 2017, p. 109.
- Ertz et al. 2017, p. 131.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 159.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2017, p. 86.
- Simon et al. 2020, p. 82.
- Sobreira et al. 2018, p. 67.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2017, p. 87.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2017, p. 90.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2017, p. 96.
- Grube, Matzer & Hafellner 1995, p. 28.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 89.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2017, p. 105.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 98.
- Sodamuk et al. 2017, p. 15.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2021, p. 372.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2021, p. 375.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 149.
- Kalb & Aptroot 2021, p. 5.
- Bungartz, Søchting & Arup 2021.
- Etayo 2017, p. 335.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 160.
- Davydov et al. 2021, p. 245.
- Lendemer, Stone & Tripp 2017, p. 459.
- Ertz et al. 2018, p. 170.
- Cáceres et al. 2017, p. 206.
- Wijayawardene et al. 2022, p. 38.
- Grube 2018, p. 695.
- Jiang et al. 2020, p. 1.
- Kondratyuk et al. 2016, p. 104.
- Díaz-Escandón et al. 2021, p. 501.
- Lücking et al. 2009, p. 411.
- Lücking, Hodkinson & Leavitt 2016, p. 370.
- Dobson 2011, p. 470.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 16.
- The British Lichen Society 2022a.
- Temu et al. 2019, p. 1.
- Kantvilas 1996, p. 229.
- Dobson 2011, p. 26.
- Sanders 2001, p. 1033.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 17.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 18.
- The British Lichen Society 2022b.
- Lendemer, Buck & Harris 2016, p. 441.
- Upreti & Rai 2013, p. 2.
- Lücking 2008, p. 4.
- Lücking 1998, p. 287.
- Rosentreter 1993, p. 333.
- Schultz, Zedda & Rambold 2009, p. 315.
- Purvis 2000, p. 5.
- Rikkinen 2015, p. 973.
- Goga et al. 2018, p. 1.
- Truong & Clerc 2003, p. 52.
- Merriam-Webster.
- International Association for Lichenology.
- Pfister 1985, p. 1.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 84.
- Brodo, Sharnoff & Sharnoff 2001, p. 103.
- Lawrey & Diederich 2003, p. 80.
- Nimis, Scheidegger & Wolseley 2002.
- Oliver 2011, p. 1.
- Field Museum 2022.
- Turner 1977, p. 461.
- Penguin Books.
- Ivanova & Ivanov 2009, p. 11.
- Vinayaka & Krishnamurthy 2012, p. 265.
References
- Aptroot, A.; Sparrius, L.B.; Alvarado, P. (2018). "Aquacidia, a new genus to accommodate a group of skiophilous temperate Bacidia species that belong in the Pilocarpaceae (lichenized ascomycetes)". Gorteria. 40: 11–14. ISSN 2542-8578.

- "Awards". International Association for Lichenology. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- Baron, George (1999). Understanding Lichens. Slough: Richmond Publishing. ISBN 978-0-85546-252-9.
- Bendre, Ashok M. (2010). A Text Book of Practical Botany. New Dehli: Rastogi Publications. ISBN 978-81-7133-923-5.
- Bowler, P. A.; Rundel, P. W. (June 1975). "Reproductive strategies in lichens". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 70 (4): 325–340. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.1975.tb01653.x.
- Brodo, Irwin M.; Sharnoff, Sylvia Duran; Sharnoff, Stephen (2001). Lichens of North America. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-08249-4.
- Bungartz, F.; Søchting, U.; Arup, U. (December 2021). "Obscuroplaca gen. nov. – a replacement name for Phaeoplaca; Teloschistaceae (lichenized Ascomycota) from the Galapagos Islands". Plant and Fungal Systematics. 66 (2): 240–241. doi:10.35535/pfsyst-2021-0022. S2CID 245619926.
- Cáceres, Marcela Eugenia da Silva; Aptroot, André; Mendonça, Cléverton Oliveira; Santos, Lidiane Alves; Lücking, Robert (2017). "Sprucidea, a further new genus of rain forest lichens in the family Malmideaceae (Ascomycota)". Bryologist. 120 (2): 202–211. doi:10.1639/0007-2745-120.2.202. S2CID 90645323.
- Chen, Jie; Blume, Hans-Peter; Beyer, Lothar (March 2000). "Weathering of rocks induced by lichen colonization — a review". Catena. 39 (2): 121–146. doi:10.1016/S0341-8162(99)00085-5.
- Davydov, Evgeny A.; Yakovchenko, Lidia S.; Hollinger, Jason; Bungartz, Frank; Parrinello, Christian; Printzen, Christian (2021). "The new genus Pulvinora (Lecanoraceae) for species of the 'Lecanora pringlei' group, including the new species Pulvinora stereothallina". The Bryologist. 124 (2): 242–256. doi:10.1639/0007-2745-124.2.242. S2CID 235188598.
- Díaz-Escandón, David; Hawksworth, David L.; Powell, Mark; Resl, Philipp; Spribille, Toby (February 2021). "The British chalk specialist Lecidea lichenicola auct. revealed as a new genus of Lichinomycetes". Fungal Biology. 125 (7): 495–504. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2021.01.007. PMID 34140146. S2CID 234008195.
- Diederich, Paul; Ertz, Damien (2020). "First checklist of lichens and lichenicolous fungi from Mauritius, with phylogenetic analyses and description of new taxa". Plant and Fungal Systematics. 65 (1): 13–75. doi:10.35535/pfsyst-2020-0003.
- Divakar, Pradeep K.; Crespo, Ana; Kraichak, Ekaphan; Leavitt, Steven D.; Singh, Garima; Schmitt, Imke; Lumbsch, H. Thorsten (2017). "Using a temporal phylogenetic method to harmonize family- and genus-level classification in the largest clade of lichen-forming fungi". Fungal Diversity. 84: 101–117. doi:10.1007/s13225-017-0379-z. S2CID 40674310.
- Dobson, Frank S. (2011). Lichens: An Illustrated Guide to the British and Irish Species. Slough, UK: Richmond Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-85546-316-8.
- Ertz, Damien; Søchting, Ulrik; Gadea, Alice; Charrier, Maryvonne; Poulsen, Roar S. (2017). "Ducatina umbilicata gen. et sp. nov., a remarkable Trapeliaceae from the subantarctic islands in the Indian Ocean". The Lichenologist. 49 (2): 127–140. doi:10.1017/s0024282916000700. S2CID 90273663.
- Ertz, Damien; Sanderson, Neil; Łubek, Anna; Kukwa, Martin (March 2018). "Two new species of Arthoniaceae from old-growth European forests, Arthonia thoriana and Inoderma sorediatum, and a new genus for Schismatomma niveum". The Lichenologist. 50 (2): 161–172. doi:10.1017/S0024282917000688.
- Etayo, Javier (2017). Hongos liquenícolas de Ecuador (PDF). Opera Lilloana (in Spanish). San Miguel de Tucumán, Argentina: Fundación Miguel Lillo.
- Favor, Lesli J. (2005). Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cell Structures: Understanding Cells with and Without a Nucleus. New York: Rosen Publishing Group. ISBN 978-1-4042-0323-5.
- Field Museum (15 February 2022). "Lichens are in danger of losing the evolutionary race with climate change". Phys.org. Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- Fryday, Alan M.; Medeiros, Ian D.; Siebert, Stefan J.; Pope, Nathaniel; Rajakaruna, Nishanta (2020). "Burrowsia, a new genus of lichenized fungi (Caliciaceae), plus the new species B. cataractae and Scoliciosporum fabisporum, from Mpumalanga, South Africa". South African Journal of Botany. 132: 471–481. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2020.06.001.
- Galloway, D. J. (2012). "Lichen biogeography". In Nash III, Thomas H. (ed.). Lichen Biology. Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 315–335. ISBN 978-0-521-69216-8.
- Gamundí, Irma J.; Spinedi, H. A. (1985). "Phaneromyces Speg. & Hariot, a discomycetous genus of critical taxonomic position" (PDF). Sydowia. 38: 106–113.
- "Glossary of Terms". The British Lichen Society. 2022b. Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- Goga, Michal; Elečko, Ján; Marcinčinová, Margaréta; Ručová, Dajana; Bačkorová, Miriam; Bačkor, Martin (2018). "Lichen Metabolites: An Overview of Some Secondary Metabolites and Their Biological Potential". In Merillon, J. M.; Ramawat, K. (eds.). Bioactive Molecules in Food. Reference Series in Phytochemistry. Springer, Cham. pp. 1–36. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-76887-8_57-1. ISBN 978-3-319-76887-8.
- Green, T. G. Allen; Pintado, Ana; Raggio, Jose; Sancho, Leopoldo Garcia (May 2018). "The lifestyle of lichens in soil crusts". The Lichenologist. 50 (3): 397–410. doi:10.1017/S0024282918000130. S2CID 90874682.
- Grube, M.; Matzer, M.; Hafellner, J. (January 1995). "A Preliminary Account of the Lichenicolous Arthonia Species with Reddish, K+ Reactive Pigments". The Lichenologist. 27 (1): 25–42. doi:10.1006/lich.1995.9999.
- Grube, Martin (October 2018). "Staurospora, a new genus for a unique species with spherical ascospores in Arthoniaceae". Herzogia. 31 (p1): 695–699. doi:10.13158/heia.31.1.2018.695. S2CID 198159947.
- Hale, Mason E., ed. (1983). The Biology of Lichens (3rd ed.). London: Edward Arnold Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7131-2867-3.
- Hawksworth, David Leslie; Sutton, Brian Charles; Ainsworth, Geoffrey Clough, eds. (1983). Ainsworth & Bisby's dictionary of the fungi, including lichens (7th ed.). Kew, Surrey: Commonwealth Mycological Institute. ISBN 978-0-85198-515-2.
- Henriksson, Elisabet; Simu, Barbro (1971). "Nitrogen Fixation by Lichens". Oikos. 22 (1): 119–121. doi:10.2307/3543371. JSTOR 3543371.
- Honegger, Rosmarie (May 1998). "The Lichen Symbiosis – What is so Spectacular about it?" (PDF). The Lichenologist. 30 (3): 193–212. doi:10.1017/s002428299200015x.
- Ivanova, Diana; Ivanov, Dobri (2009). "Ethnobotanical use of lichens: lichens for food review". Scripta Scientifica Medica. 41 (1): 11–16. doi:10.14748/ssm.v41i1.456.
- Jiang, Shu Hua; Hawksworth, David L.; Lücking, Robert; Wei, Jiang Chun (2020). "A new genus and species of foliicolous lichen in a new family of Strigulales (Ascomycota: Dothideomycetes) reveals remarkable class-level homoplasy". IMA Fungus. 11 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1186/s43008-019-0026-2. PMC 7325298. PMID 32617253.
- Kalb, Klaus; Aptroot, André (2021). "New lichens from Africa" (PDF). Archive for Lichenology. 28: 1–12.
- Kantvilas, Gintaras (May 1996). "A new byssoid lichen genus from Tasmania" (PDF). The Lichenologist. 28 (3): 229–237. doi:10.1006/lich.1996.0020. S2CID 85573550. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 October 2014.
- Kantvilas, Gintaras; Wedin, Mats; Svensson, Måns (2021). "Australidea (Malmideaceae, Lecanorales), a new genus of lecideoid lichens, with notes on the genus Malcolmiella". The Lichenologist. 53 (5): 395–407. doi:10.1017/s0024282921000311. S2CID 238638591.
- Kondratyuk, S.Y.; Lőkös, L.; Halda, J.P.; Haji Moniri, M.; Farkas, E.; Park, J.S.; Lee, B.G.; Oh, S.O.; Hur, J.S. (2016). "New and noteworthy lichen-forming and lichenicolous fungi 4". Acta Botanica Hungarica. 58 (1–2): 75–136. doi:10.1556/034.58.2016.1-2.4.
- Kondratyuk, S.Y.; Lőkös, L.; Upreti, D. K.; Nayaka, S.; Mishra, G.K.; Ravera, S.; Jeong, M.-H.; Jang, S.-H.; Park, J.S.; Hur, J.-S. (2017). "New monophyletic branches of the Teloschistaceae (lichen-forming Ascomycota) proved by three gene phylogeny" (PDF). Acta Botanica Hungarica. 59 (1–2): 71–136. doi:10.1556/034.59.2017.1-2.6. hdl:10447/414429.
- Kondratyuk, S.Y.; Lőkös, L.; Kärnefelt, I.; Thell, A.; Jeong, M.-H.; Oh, S.-O.; Kondratiuk, A.S.; Farkas, E.; Hur, J.-S. (2021). "Contributions to molecular phylogeny of lichen-forming fungi 2. Review of current monophyletic branches of the family Physciaceae" (PDF). Acta Botanica Hungarica. 63 (3–4): 351–390. doi:10.1556/034.63.2021.3-4.8. S2CID 239503884.
- Kraichak, E.; Huang, J.P.; Nelsen, M.; Leavitt, S.D.; Lumbsch, H.T. (2018). "A revised classification of orders and families in the two major subclasses of Lecanoromycetes (Ascomycota) based on a temporal approach". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 20: 1–17. doi:10.1093/botlinnean/boy060/5091569. S2CID 92280920.
- Kraichak, E.; Huang, J.P.; Nelsen, M.; Leavitt, S.D.; Lumbsch, H.T. (12 September 2018). "Nomenclatural novelties" (PDF). Index Fungorum. 375: 1. ISSN 2049-2375.
- Kistenich, Sonja; Timdal, Einar; Bendiksby, Mika; Ekman, Stefan (2018). "Molecular systematics and character evolution in the lichen family Ramalinaceae (Ascomycota: Lecanorales)". Taxon. 67 (5): 871–904. doi:10.12705/675.1. hdl:10852/67955.
- Laundon, Jack R. (1986). Lichens. Shire Natural History series. Princes Risborough: Shire Publications. ISBN 978-0-85263-811-8.
- Lawrey, James D.; Diederich, Paul (Spring 2003). "Lichenicolous Fungi: Interactions, Evolution, and Biodiversity". The Bryologist. 106 (1): 80–120. doi:10.1639/0007-2745(2003)106[0080:LFIEAB]2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 3244800. S2CID 85790408.
- Lendemer, James; Harris, Richard C.; Ruiz, Ana Maria (March 2016). "A Review of the Lichens of the Dare Regional Biodiversity Hotspot in the Mid-Atlantic Coastal Plain of North Carolina, Eastern North America". Castanea. 81 (1): 1–77. doi:10.2179/15-073R2.
- Lendemer, James C.; Buck, William R.; Harris, Richard C. (September 2016). "Two new host-specific hepaticolous species of Catinaria (Ramalinaceae)". The Lichenologist. 48 (5): 441–449. doi:10.1017/S0024282916000438. S2CID 89433929.
- Lendemer, James C.; Stone, Heather B.; Tripp, Erin A. (2017). "Taxonomic delimitation of the rare, eastern North American endemic lichen Santessoniella crossophylla (Pannariaceae)". The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society. 144 (4): 459–468. doi:10.3159/torrey-d-16-00009.1. JSTOR 26305705. S2CID 90392751.
- Lepp, Heino (2014). "Basidiolichens". Australian Lichens. Australian National Herbarium and Australian National Botanic Gardens. Retrieved 20 August 2022.
- Li, Xi; Hou, Zheng; Xu, Chenjie; Shi, Xuan; Yang, Lingxiao; Lewis, Louise A.; Zhong, Bojian (July 2021). "Large Phylogenomic Data sets Reveal Deep Relationships and Trait Evolution in Chlorophyte Green Algae". Genome Biology and Evolution. 13 (7): 329–332. doi:10.1093/gbe/evab101. PMC 8271138. PMID 8271138.
- "Lichen". Cambridge Dictionary. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- "Lichen Morphology". The British Lichen Society. 2022a. Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- "Lichenology". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 20 August 2022.
- Lücking, Robert (May 1998). "'Plasticolous' Lichens in a Tropical Rain Forest at La Selva Biological Station, Costa Rica". The Lichenologist. 30 (3): 287–291. doi:10.1006/lich.1998.0124. S2CID 250348579.
- Lücking, Robert (2008). "Foliicolous Lichenized Fungi". Flora Neotropica. 103: 1–866. ISSN 0071-5794. JSTOR 25660968.
- Lücking, Robert; Hodkinson, Brendan P.; Leavitt, Steven D. (Winter 2016). "The 2016 classification of lichenized fungi in the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota–Approaching one thousand genera". The Bryologist. 119 (4): 361–416. doi:10.1639/0007-2745-119.4.361. JSTOR 44250015. S2CID 90258634.
- Lücking, Robert; Hodkinson, Brendan P.; Leavitt, Steven D. (2017). "Corrections and amendments to the 2016 classification of lichenized fungi in the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota". The Bryologist. 120 (1): 58–69. doi:10.1639/0007-2745-120.1.058. JSTOR 44820821. S2CID 90363578.
- Lücking, Robert; Kalb, Klause (2018). "Formal instatement of Allographa (Graphidaceae): how to deal with a hyperdiverse genus complex with cryptic differentiation and paucity of molecular data". Herzogia. 31 (p1): 535–561. doi:10.13158/heia.31.1.2018.535. S2CID 217375498.
- Lücking, Robert; Rivas-Plata, E; Chavez, JL; Umaña, L; Sipman, HJM (2009). "How many tropical lichens are there… really?". Bibliotheca Lichenologica. 100: 399–418.
- Nimis, Pier Luigi; Scheidegger, Christoph; Wolseley, Patricia A., eds. (2002). Monitoring with Lichens - Monitoring Lichens. Vol. 7. Dordrecht: Springer Science+Business. ISBN 978-94-010-0423-7.
- Oliver, Mary (March 2011). "Canaries in a coal mine: using lichens to measure nitrogen pollution" (PDF). Science Findings. USDA Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station. 131.
- Pfister, Donald H. (1985). "A bibliographic account of exsiccatae containing fungi". Mycotaxon. 23: 1–139.
- Purvis, William (2000). Lichens. Life Series. London: The Natural History Museum. ISBN 978-0-565-09153-8.
- Rikkinen, Jouko (April 2015). "Cyanolichens". Biodiversity and Conservation. 24 (4): 973–993. doi:10.1007/s10531-015-0906-8. S2CID 254277998.
- Rosentreter, Roger (Autumn 1993). "Vagrant Lichens in North America". The Bryologist. 96 (3): 333–338. doi:10.2307/3243861. JSTOR 3243861.
- Sanders, William B. (December 2001). "Lichens: the interface between mycology and plant morphology". BioScience. 51 (12): 1025–1035. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[1025:LTIBMA]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 52255499.
- Schultz, Matthias; Zedda, Luciana; Rambold, Gerhard (2009). "New records of lichen taxa from Namibia and South Africa Bibliotheca Lichenologica" (PDF). In Aptroot, André; Seaward, Mark R.D.; Sparrius, Laurens B. (eds.). Biodiversity and ecology of lichens – Liber Amicorum Harrie Sipman. Vol. 99. Berlin and Stuttgart: J. Cramer. pp. 315–334.
- Silverstein, Alvin; Silverstein, Virginia B.; Silverstein, Robert A. (1996). Fungi. New York: Twenty-First Century Books. ISBN 978-0-8050-3520-9.
- Simon, Antoine; Lücking, Robert; Moncada, Bibiana; Mercado-Díaz, Joel A.; Bungartz, Frank; da Silva Cáceres, Marcela Eugenia; Gumboski, Emerson Luiz; de Azevedo Martins, Suzana Maria; Spielmann, Adriano; Parker, Dinah; Goffinet, Bernard (2020). "Emmanuelia, a new genus of lobarioid lichen-forming fungi (Ascomycota: Peltigerales): phylogeny and synopsis of accepted species". Plant and Fungal Systematics. 65 (1): 76–94. doi:10.35535/pfsyst-2020-0004.
- Smith, C. W.; Aptroot, A.; Coppins, B. J.; Fletcher, A.; Gilbert, O. L.; James, P. W.; Wolseley, P. A., eds. (2009). The Lichens of Great Britain and Ireland. London: The British Lichen Society. ISBN 978-0-9540418-8-5.
- Smith, Hayden B.; Dal Grande, Francesco; Muggia, Lucia; Keuler, Rachel; Divakar, Pradeep K.; Grewe, Felix; Schmitt, Imke; Lumbsch, H. Thorsten; Leavitt, Steven D. (November 2020). "Metagenomic data reveal diverse fungal and algal communities associated with the lichen symbiosis". Symbiosis. 82 (1–2): 133–147. doi:10.1007/s13199-020-00699-4. S2CID 214724803.
- Sobreira, Priscylla Nayara Bezerra; Cáceres, Marcela Eugenia Da Silva; Maia, Leonor Costa; Lücking, Robert (July 2018). "Flabelloporina, a new genus in the Porinaceae (Ascomycota, Ostropales), with the first record of F. squamulifera from Brazil". Phytotaxa. 538 (1): 67–75. doi:10.11646/phytotaxa.358.1.4. S2CID 89707839.
- Sodamuk, Mattika; Boonpragob, Kansri; Mongkolsuk, Pachara; Tehler, Andrs; Leavitt, Steven D.; Lumbsch, H. Thorsten (2017). "Kalbionora palaeotropica, a new genus and species from coastal forests in Southeast Asia and Australia (Malmideaceae, Ascomycota)". MycoKeys. 22: 15–25. doi:10.3897/mycokeys.22.12528.
- Spribille, Toby; Fryday, Alan M.; Pérez-Ortega, Sergio; Svensson, Måns; Tønsberg, Tor; Ekman, Stefan; Holien, Håkon; Resl, Philipp; Schneider, Kevin; Stabentheiner, Edith; Thüs, Holger; Vondrák, Jan; Sharman, Lewis (March 2020). "Lichens and associated fungi from Glacier Bay National Park, Alaska". The Lichenologist. 52 (2): 61–181. doi:10.1017/S0024282920000079. PMID 32788812.
- Temu, Stella Gilbert; Tibell, Sanja; Tibuhwa, Donatha Damian; Tibell, Leif (October 2019). "Crustose calicioid lichens and fungi in mountain cloud forests of Tanzania". Microorganisms. 7 (11): 491. doi:10.3390/microorganisms7110491. PMC 6920850. PMID 31717781.
- "Trouble with Lichen". Penguin Books. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- Truong, Camille; Clerc, Philippe (2003). "The Parmelia borreri group (lichenized ascomycetes) in Switzerland". Botanica Helvetica. 113 (1): 49–61.
- Turner, Nancy J. (October 1977). "Economic importance of black tree lichen (Bryoria fremontii) to the Indians of western North America". Economic Botany. 31 (4): 461–470. doi:10.1007/BF02912559. JSTOR 4253875. S2CID 29530274.
- Upreti, Dalip K.; Rai, Himanshu, eds. (2013). Terricolous Lichens in India. Vol. 1: Diversity Patterns and Distribution Ecology. New York: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4614-8736-4.
- Van Hoose, Natalie (21 July 2021). "Yeast emerges as hidden third partner in lichen symbiosis". Purdue University News. Purdue University.
- Vinayaka, K. S.; Krishnamurthy, Y. L. (2012). "Ethno-lichenological Studies of Shimoga and Mysore Districts, Karnataka, India". Advances in Plant Sciences. 25 (1): 265–267.
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Dai, D.Q.; Sánchez-García, M.; Goto, B.T.; Saxena, R.K.; et al. (2022). "Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa – 2021". Mycosphere. 13 (1): 53–453. doi:10.5943/mycosphere/13/1/2. S2CID 249054641.
- Wilk, Karina; Pabijan, Maciej; Saługa, Marta; Gaya, Ester; Lücking, Robert (2021). "Phylogenetic revision of South American Teloschistaceae (lichenized Ascomycota, Teloschistales) reveals three new genera and species". Mycologia. 113 (2): 278–299. doi:10.1080/00275514.2020.1830672. PMID 33428561. S2CID 231586897.
- Zakeri, Zakieh; Junne, Stefan; Jäger, Fabian; Dostert, Marcel; Otte, Volker; Neubauer, Peter (May 2022). "Lichen cell factories: methods for the isolation of photobiont and mycobiont partners for defined pure and co-cultivation". Microbial Cell Factories. 21 (1): 80. doi:10.1186/s12934-022-01804-6. PMC 9082883. PMID 35534897.
