Etilamfetamine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral, sublingual, insufflated, inhaled (vaporized), intravenous, rectal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.711 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H17N |
| Molar mass | 163.264 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Etilamfetamine (trade names Apetinil and Adiparthrol; also known as N-ethylamphetamine) is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was invented in the early 20th century and was subsequently used as an anorectic or appetite suppressant in the 1950s,[1] but was not as commonly used as other amphetamines such as amphetamine, methamphetamine, and benzphetamine, and was largely discontinued once newer drugs such as phenmetrazine were introduced. It most likely acts primarily as a dopamine releasing agent.[2] Its activity as a norepinephrine or serotonin releasing agent is not known.
Chemistry
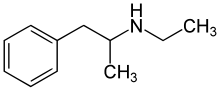
The molecular structure of ethylamphetamine is analogous to methamphetamine, with an ethyl group in place of the methyl group.[Note 1] It can also be considered a substituted amphetamine, with an ethyl group on the amphetamine backbone.[Note 2][Note 3]
Recreational Use
Ethylamphetamine can be used as a recreational drug and, while its prevalence is less than amphetamine's, it is still encountered as a substance taken for recreational purposes.
Ethylamphetamine produces effects similar to amphetamine and methamphetamine, though its potency is less. At equipotent dosage, ethylamphetamine is subjectively less euphorigenic.
See also
References
- ↑ Junet R (October 1956). "[Ethylamphetamine in the treatment of obesity]". Praxis. 45 (43): 986–8. PMID 13389142.
- ↑ Reith ME, Blough BE, Hong WC, Jones KT, Schmitt KC, Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Rothman RB, Katz JL (February 2015). "Behavioral, biological, and chemical perspectives on atypical agents targeting the dopamine transporter". Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 147: 1–19. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.12.005. PMC 4297708. PMID 25548026.
Notes
- ↑ Amphetamine is a substituted phenethylamine with a methyl group at RA position.
- ↑ The ethyl group of ethylamphetamine is at RN position, hence the name N-ethylamphetamine.
- ↑ Ethylamphetamine is structurally similar to N-methylamphetamine (methamphetamine), the ethyl group being replaced in methamphetamine with a methyl group.