Levoamphetamine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
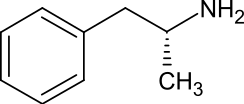
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2R)-1-Phenylpropan-2-amine[1] | |
| Other names
L-Amphetamine, Levamfetamine[2] | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
Beilstein Reference |
2432739 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.320 |
| EC Number |
|
Gmelin Reference |
1125855 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C9H13N |
| Molar mass | 135.2062 g mol−1 |
| log P | 1.789 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Oral (as part of Adderall, Evekeo, and generic amphetamine sulfate[3][4]) | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Levoamphetamine[note 1] is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Pharmaceuticals that contain levoamphetamine are currently indicated and prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obesity, and narcolepsy in some countries.
Levoamphetamine is the levorotatory stereoisomer of the amphetamine molecule. While pharmaceutical formulations containing enantiopure levoamphetamine are no longer manufactured, levomethamphetamine (levmetamfetamine) is still marketed and sold over-the-counter as a nasal decongestant.
Chemistry
Levoamphetamine is the levorotatory stereoisomer of the amphetamine molecule. Racemic amphetamine contains two optical isomers, dextroamphetamine, and levoamphetamine.[6][7]
Formulations
Racemic amphetamine
The first patented amphetamine brand, Benzedrine, was a racemic (i.e., equal parts) mixture of the free bases or sulfate salts of both amphetamine enantiomers (levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine) that was introduced in the United States in 1934 as an inhaler for treating nasal congestion.[3] It was later realized that the amphetamine enantiomers could treat obesity, narcolepsy, and ADHD.[3][4] Because of the greater central nervous system effect of the dextrorotatory enantiomer (i.e., dextroamphetamine), sold as Dexedrine, prescription of the Benzedrine brand fell and was eventually discontinued.[8] However, in 2012, racemic amphetamine sulfate was reintroduced as the Evekeo brandname.[4][9]
Adderall
Adderall is a 3.1:1 mixture of dextro- to levo- amphetamine base equivalent pharmaceutical that contains equal amounts (by weight) of four salts: dextroamphetamine sulfate, amphetamine sulfate, dextroamphetamine saccharate and amphetamine (D,L)-aspartate monohydrate. This result is a 76% dextroamphetamine to 24% levoamphetamine, or ¾ to ¼ ratio.[6][7]
Evekeo
Evekeo is an FDA-approved medication that contains racemic amphetamine sulfate (i.e., 50% levoamphetamine sulfate and 50% dextroamphetamine sulfate).[4] It is approved for the treatment of narcolepsy, ADHD, and exogenous obesity.[4] The orally disintegrating tablets are approved for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents aged six to 17 years of age.[10]
Others
Products using amphetamine base are now marketed. Dyanavel XR, a liquid suspension form became available in 2015, and contains about 24% levoamphetamine.[11] Adzenys XR, an orally dissolving tablet came to market in 2016 and contains 25% levoamphetamine.[12][13]
Enantiopure levoamphetamine succinate was sold in Hungary between 1952 and 1955 under the brand name Cydril.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Synonyms and alternate spellings include: (2R)-1-phenylpropan-2-amine (IUPAC name), levamfetamine (International Nonproprietary Name [INN]), (R)-amphetamine, (−)-amphetamine, l-amphetamine, and L-amphetamine.[1][5]
References
- 1 2 "L-Amphetamine". PubChem Compound. United States National Library of Medicine – National Center for Biotechnology Information. 30 December 2017. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ↑ CID 32893 from PubChem
- 1 2 3 Heal DJ, Smith SL, Gosden J, Nutt DJ (June 2013). "Amphetamine, past and present – a pharmacological and clinical perspective". J. Psychopharmacol. 27 (6): 479–496. doi:10.1177/0269881113482532. PMC 3666194. PMID 23539642.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Evekeo- amphetamine sulfate tablet". DailyMed. 14 August 2019. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ↑ "R(-)amphetamine". IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- 1 2 "Adderall XR- dextroamphetamine sulfate, dextroamphetamine saccharate, amphetamine sulfate and amphetamine aspartate capsule, extended release". DailyMed. 17 July 2019. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- 1 2 "Adderall- dextroamphetamine saccharate, amphetamine aspartate, dextroamphetamine sulfate, and amphetamine sulfate tablet". DailyMed. 8 November 2019. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ↑ "Benzedrine: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- ↑ "Evekeo: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ "Evekeo ODT- amphetamine sulfate tablet, orally disintegrating". DailyMed. 20 February 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ↑ "Adzenys XR-ODT- amphetamine tablet, orally disintegrating". DailyMed. 22 January 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
Adzenys XR-ODT (amphetamine extended-release orally disintegrating tablet) contains a 3 to 1 ratio of d- to l-amphetamine, a central nervous system stimulant.
- ↑ "Adzenys ER- amphetamine suspension, extended release". DailyMed. 21 January 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
External links
- "Amphetamine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Amphetamine sulfate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Amphetamine aspartate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Dextroamphetamine saccharate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Amphetamine". MedlinePlus.