Ethinylestradiol/megestrol acetate
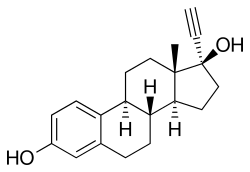 Ethinylestradiol | |
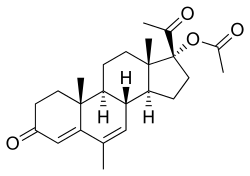 Megestrol acetate | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Ethinylestradiol | Estrogen |
| Megestrol acetate | Progestogen; Progestin |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Nuvacon, Volidan |
| Other names | EE/MGA |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Progestin; Progestogen |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
Ethinylestradiol/megestrol acetate (EE/MGA), sold under the brand name Volidan among others, was a combination of ethinylestradiol (EE), an estrogen, and megestrol acetate (MGA), a progestin, which was used as a birth control pill to prevent pregnancy in women.[1][2] It was taken by mouth and contained 50 to 100 μg EE and 1 to 5 mg MGA per tablet.[2][1] MGA-containing birth control pills were withdrawn after reports in the early 1970s of a high incidence of venous thromboembolism in association with the preparations.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 Lara Marks (2001). Sexual Chemistry: A History of the Contraceptive Pill. Yale University Press. pp. 77–78. ISBN 978-0-300-08943-1.
- 1 2 Mears E (1963). "A new type of oral contraceptive". Br Med J. 1 (5341): 1318–20. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.5341.1318. PMC 2123904. PMID 13934321.
- ↑ El Makhzangy MN, Wynn V, Lawrence DM (January 1979). "Sex hormone binding globulin capacity as an index of oestrogenicity or androgenicity in women on oral contraceptive steroids". Clinical Endocrinology. 10 (1): 39–45. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1979.tb03031.x. PMID 571314. S2CID 7262495.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.