Monoamine precursor
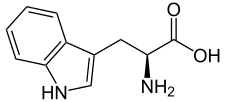
Monoamine precursors are precursors of monoamines and monoamine neurotransmitters in the body.[1][2] The amino acids L-tryptophan and L-5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP; oxitriptan) are precursors of serotonin and melatonin, while the amino acids L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, and L-DOPA (levodopa) are precursors of dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine (noradrenaline).[1][2] Administration of monoamine precursors can increase the levels of monoamine neurotransmitters in the body and brain.[2] Monoamine precursors may be used in combination with peripherally selective aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitors (AAAD inhibitors; also known as DOPA decarboxylase (DDC) inhibitors) such as carbidopa and benserazide.[3] Carbidopa/levodopa is used to increase brain dopamine levels in the treatment of Parkinson's disease[3] while carbidopa/oxitriptan (EVX-101) is under development as an antidepressant for possible use in the treatment of depression.[4]
References
- Kohlstadt, Ingrid (19 April 2016). Food and Nutrients in Disease Management. ISBN 9781420067637.
- Fernandes, John; Saudubray, Jean-Marie; Berghe, Georges van den; Walter, John H. (22 November 2006). Inborn Metabolic Diseases: Diagnosis and Treatment. ISBN 9783540287858.
- Salat D, Tolosa E (January 2013). "Levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: current status and new developments". J Parkinsons Dis. 3 (3): 255–69. doi:10.3233/JPD-130186. PMID 23948989.
- "Carbidopa/Oxytriptan - Evecxia - AdisInsight".
| Types |
|
|---|---|
| Vitamins and chemical elements ("minerals") | |
| Other common ingredients |
|
| Related articles | |