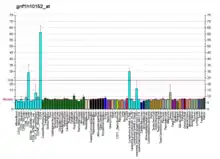
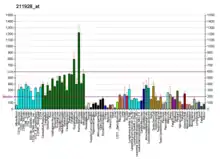
DYNC1H1
DYNC1H1 (Dynein cytoplasmic 1 heavy chain 1) هوَ بروتين يُشَفر بواسطة جين DYNC1H1 في الإنسان.[1][2][3]
المراجع
- "Mammalian cells express three distinct dynein heavy chains that are localized to different cytoplasmic organelles"، J Cell Biol، 133 (4): 831–42، أغسطس 1996، doi:10.1083/jcb.133.4.831، PMC 2120833، PMID 8666668.
- "Entrez Gene: DYNC1H1 dynein, cytoplasmic 1, heavy chain 1"، مؤرشف من الأصل في 05 ديسمبر 2010.
- "Cytoplasmic dynein nomenclature"، J Cell Biol، 171 (3): 411–3، نوفمبر 2005، doi:10.1083/jcb.200508078، PMC 2171247، PMID 16260502.
قراءة متعمقة
- "Localization of the human cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain (DNECL) to 14qter by fluorescence in situ hybridization."، Genomics، 22 (3): 660–1، 1995، doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1447، PMID 8001984.
- "Cytoplasmic dynein plays a role in mammalian mitotic spindle formation."، J. Cell Biol.، 123 (4): 849–58، 1993، doi:10.1083/jcb.123.4.849، PMC 2200153، PMID 8227145.
- "Multiple mouse chromosomal loci for dynein-based motility."، Genomics، 36 (1): 29–38، 1997، doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0422، PMID 8812413.
- "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery."، Genome Res.، 6 (9): 791–806، 1997، doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791، PMID 8889548.
- "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro."، DNA Res.، 4 (2): 141–50، 1997، doi:10.1093/dnares/4.2.141، PMID 9205841.
- "Identification of dynein heavy chain genes expressed in human and mouse testis: chromosomal localization of an axonemal dynein gene."، Gene، 200 (1–2): 193–202، 1997، doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00417-4، PMID 9373155.
- "Role of cytoplasmic dynein in melanosome transport in human melanocytes."، J. Invest. Dermatol.، 114 (5): 990–7، 2000، doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00957.x، PMID 10771482.
- "Immunolocalization of cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin subunits in cultured macrophages: enrichment on early endocytic organelles."، J. Cell Sci.، 114 (Pt 1): 229–240، 2001، PMID 11112706.
- "A LIS1/NUDEL/cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain complex in the developing and adult nervous system."، Neuron، 28 (3): 681–96، 2001، doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00146-X، PMID 11163259.
- "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences."، Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.، 99 (26): 16899–903، 2003، Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M، doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899، PMC 139241، PMID 12477932.
- "Preferentially localized dynein and perinuclear dynactin associate with nuclear pore complex proteins to mediate genomic union during mammalian fertilization."، J. Cell Sci.، 116 (Pt 23): 4727–38، 2004، doi:10.1242/jcs.00784، PMID 14600259.
- "Role of cytoplasmic dynein in perinuclear aggregation of phagocytosed melanosomes and supranuclear melanin cap formation in human keratinocytes."، J. Invest. Dermatol.، 121 (4): 813–20، 2003، doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12481.x، PMID 14632200.
- "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs."، Nat. Genet.، 36 (1): 40–5، 2004، doi:10.1038/ng1285، PMID 14702039.
- "Proteomic identification of brain proteins that interact with dynein light chain LC8."، Proteomics، 4 (2): 339–46، 2004، doi:10.1002/pmic.200300528، PMID 14760703.
- "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway."، Genome Res.، 14 (7): 1324–32، 2004، doi:10.1101/gr.2334104، PMC 442148، PMID 15231748.
- "Proteomic, functional, and domain-based analysis of in vivo 14-3-3 binding proteins involved in cytoskeletal regulation and cellular organization."، Curr. Biol.، 14 (16): 1436–50، 2004، doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.07.051، PMID 15324660.
- "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)."، Genome Res.، 14 (10B): 2121–7، 2004، doi:10.1101/gr.2596504، PMC 528928، PMID 15489334.
- "Nucleolar proteome dynamics."، Nature، 433 (7021): 77–83، 2005، Bibcode:2005Natur.433...77A، doi:10.1038/nature03207، PMID 15635413.
- بوابة علم الأحياء الخلوي والجزيئي
- بوابة الكيمياء الحيوية
- بوابة طب
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.