NIPA2
NIPA2 (NIPA magnesium transporter 2) هوَ بروتين يُشَفر بواسطة جين NIPA2 في الإنسان.[1][2]
| NIPA2 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| المعرفات | |||||||||||||||||
| الأسماء المستعارة | NIPA2, non imprinted in Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome 2, SLC57A2, NIPA magnesium transporter 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| معرفات خارجية | الوراثة المندلية البشرية عبر الإنترنت 608146 MGI: MGI:1913918 HomoloGene: 11368 GeneCards: 81614 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| نمط التعبير عن الحمض النووي الريبوزي | |||||||||||||||||
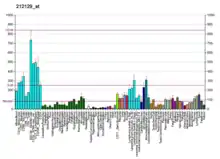 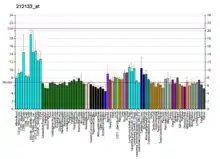 | |||||||||||||||||
| المزيد من بيانات التعبير المرجعية | |||||||||||||||||
| أورثولوج | |||||||||||||||||
| الأنواع | الإنسان | الفأر | |||||||||||||||
| أنتريه | 81614 | 93790 | |||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000140157 | ENSMUSG00000030452 | |||||||||||||||
| يونيبروت | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (مرسال ر.ن.ا.) | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (بروتين) | |||||||||||||||||
| الموقع (UCSC | n/a | Chr 7: 55.58 – 55.61 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| بحث ببمد | |||||||||||||||||
| ويكي بيانات | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
المراجع
- "Identification of four highly conserved genes between breakpoint hotspots BP1 and BP2 of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes deletion region that have undergone evolutionary transposition mediated by flanking duplicons"، Am J Hum Genet، 73 (4): 898–925، سبتمبر 2003، doi:10.1086/378816، PMC 1180611، PMID 14508708.
- "Entrez Gene: NIPA2 non imprinted in Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome 2"، مؤرشف من الأصل في 05 ديسمبر 2010.
قراءة متعمقة
- "Expression of 4 genes between chromosome 15 breakpoints 1 and 2 and behavioral outcomes in Prader-Willi syndrome"، Pediatrics، 118 (4): e1276–e1283، 2006، doi:10.1542/peds.2006-0424، PMID 16982806.
- Gerhard DS؛ Wagner L؛ Feingold EA؛ وآخرون (2004)، "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)"، Genome Res.، 14 (10B): 2121–2127، doi:10.1101/gr.2596504، PMC 528928، PMID 15489334.
- Lefèvre C؛ Bouadjar B؛ Karaduman A؛ وآخرون (2005)، "Mutations in ichthyin a new gene on chromosome 5q33 in a new form of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis"، Hum. Mol. Genet.، 13 (20): 2473–2482، doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh263، PMID 15317751.
- Glinsky GV؛ Glinskii AB؛ Stephenson AJ؛ وآخرون (2004)، "Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer"، J. Clin. Invest.، 113 (6): 913–923، doi:10.1172/JCI20032، PMC 362118، PMID 15067324.
- Ota T؛ Suzuki Y؛ Nishikawa T؛ وآخرون (2004)، "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs"، Nat. Genet.، 36 (1): 40–45، doi:10.1038/ng1285، PMID 14702039.
- Strausberg RL؛ Feingold EA؛ Grouse LH؛ وآخرون (2003)، "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences"، Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.، 99 (26): 16899–16903، doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899، PMC 139241، PMID 12477932.
- Andersson B؛ Wentland MA؛ Ricafrente JY؛ وآخرون (1996)، "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction"، Anal. Biochem.، 236 (1): 107–113، doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138، PMID 8619474.
- بوابة طب
- بوابة الكيمياء الحيوية
- بوابة علم الأحياء الخلوي والجزيئي
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.